scanloc¶
Module for locating local earthquakes and man-made seismicity by DBSCAN cluster search.
Description¶
Low-threshold monitoring¶
scanloc associates detected P and S phases from local and regional earthquakes and other seismic events for locating. It determines initial hypocenter solutions by cluster search based on DBSCAN [2]. Additional P and S phases are associated to existing internal solutions from cluster search or solutions incoming through the messaging system from external modules.
Due to the clustering and subsequent phase association scanloc facilitates low-threshold monitoring of high- and low-rate seismicity with high accuracy.
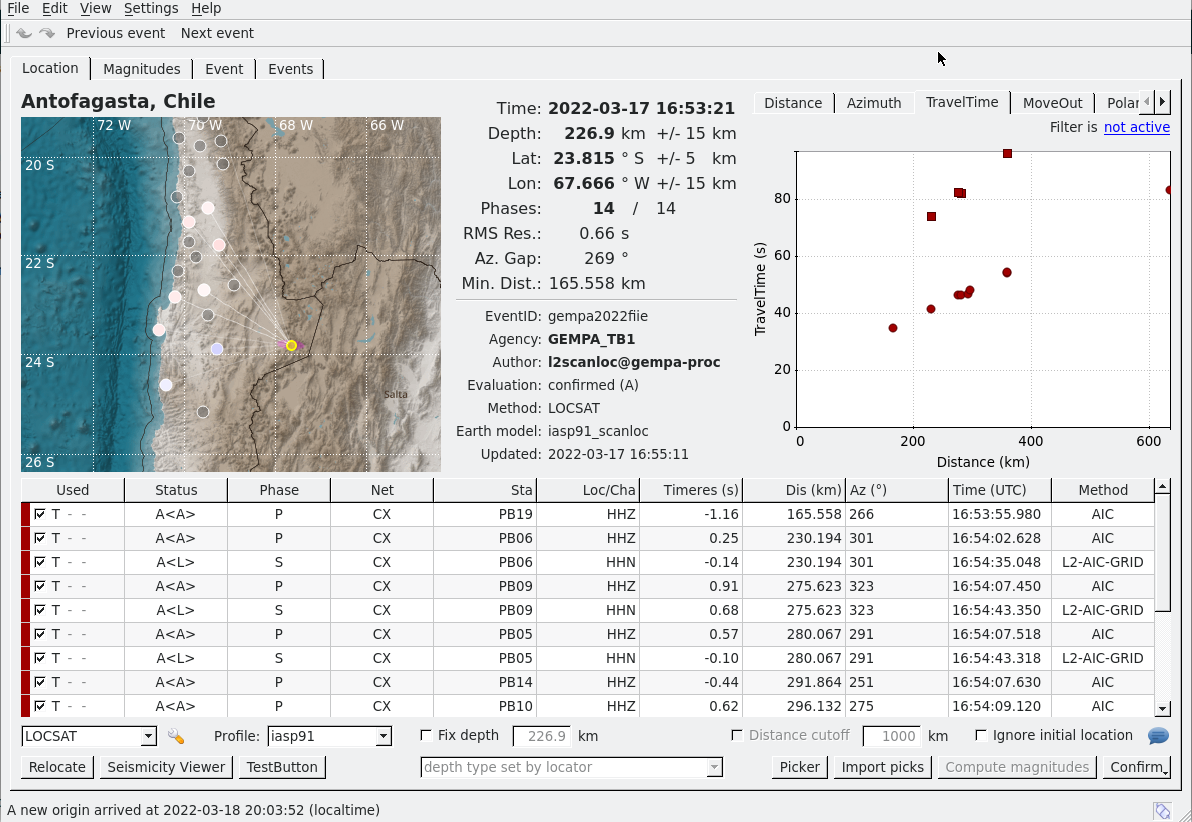
Figure 1: scolv Location tab with an automatic earthquake solution from scanloc based on P and S phases.¶
Teleseismic events¶
For teleseismic events scanloc can also be used to:
Associate more picks from P and S phases to external origins,
Suppress fake events due to detections from large earthquakes recorded by dense local networks at teleseismic distances. A dedicated section explains the setup and the requirements.
Travel-time tables¶
The scanloc package ships with densely sampled travel-time tables for LOCSAT [5] based on the IASP91 Earth model to enhance locating local earthquakes.
S phases¶
In order to deliver high-quality picks from S phases, the scanloc package also includes the saic plugin with the enhanced S-phase picker. The S-phase picker can be applied to detect S phases on the horizontal components or on the vertical component in case of 1-component sensors. In addition the scanloc package comes with the graphical debugger for the S-phase picker provided by the spickdbg plugin.
Array measurements¶
Detections from array measurements including detection time, slowness and back azimuth can be fully considered by scoring depending on the applied locator.
Auxiliary tools¶
The scanloc package also ships with auxiliary Python script for real-time or non-real-time playbacks or tuning. Read the dedicated section for more details.
Workflow¶
scanloc processes picks and origins in the following order:
Buffering of picks and origins,
Clustering of P picks:
cluster formation,
splitting of clusters in case of multiple P picks from the same station.
Clustering is skipped in case of an external origin.
Association of P and S picks to clusters and external origins.
Locating origins and formation of internal events,
Scoring of origins and setting the preferred origin accordingly of an internal events.
Evaluation and sending of the preferred origin of an internal event.
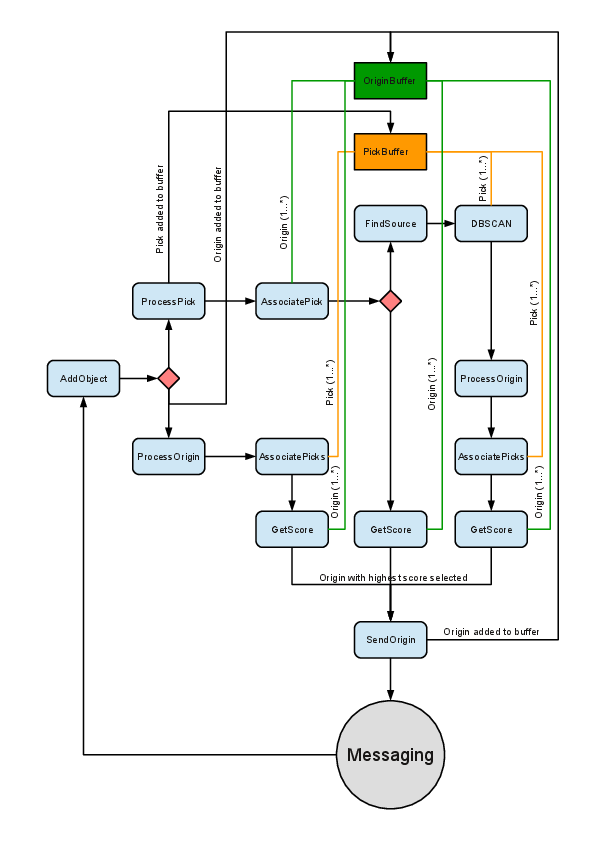
Figure 2: Simplified work flow of scanloc.¶
Pick and origin buffering¶
Note
scanloc processes picks with unique public IDs. However, the accuracy of
public IDs currently generated by scautopick [16] is limited to
10 ms by default. In systems with very frequent picks and in
pipeline systems
this limitation may result in clashes. Therefore, we recommend to let
scautopick use the same high-resolution public ID scheme as all
other modules by configuring the ID pattern explicitly in global module
configuration (global.cfg):
publicIDPattern = @classname@/@time/%Y%m%d%H%M%S.%f@.@id@
A solution for scautopick will be provided with SeisComP in a future release with version > 6.7.2.
The entry point of scanloc is the addObject method which handles incoming objects from the messaging system. By default it is subscribed to the messaging group PICK and LOCATION. Depending on which object type (pick or origin) is incoming different working steps are proceeded.
In case a pick arrives, scanloc
tests the pick:
evaluation status: Rejected picks are ignored unless the command-line option
--allow-rejected-picksis given.tests the author information against
buffer.authorWhiteList. When the parameter is configured, the pick is ignored if its authors does not matchbuffer.authorWhiteList.
adds the pick after passing the tests to the pick buffer keeping it for the time given by
buffer.pickKeepor--pick-keep,tries to use the pick for clustering,
checks if the pick can be associate to origins in the origin buffer exceeding a configurable
minScore. In case the pick can be associated, the scores for all new origins are calculated and the origin with the highest score is selected.
In case an origin arrives, scanloc
tests the origin:
tests the evaluation mode. Manual origins are ignored unless
buffer.ignoreManualOrigins= false,tests the author information against
buffer.authorWhiteListandbuffer.originAuthorWhiteList. When the parameters are configured, the origin is ignored if its authors does not match the configured values.
adds the origin after passing the tests to the origin buffer keeping it the time given by
buffer.originKeepor--origin-keepseconds,tries to associate additional picks to the origin.
Adjust the buffer.* parameters according to the times these objects
are required for processing.
Hint
You may use playback_picks for printing information on picks and amplitudes contained in XML files used, e.g., for tuning or playbacks:
playback_picks --print picks.xml
Clustering¶
In case the pick cannot be associated, the cluster search is started. The
cluster search is based on the algorithm DBSCAN [2] which
takes the required number of neighbours (clusterSearch.minSize)
and clusterSearch.maxSearchDist as configuration parameters.
The algorithm forms clusters of picks by searching for neighboring stations
that have picks. Internal origins are formed from clusters.
The number of origins from cluster search is limited by the configuration parameter
clusterSearch.maxOrigins.
The cluster search considers picks from stations by with:
where maxSearchDist is configurable by clusterSearch.maxSearchDist.
is the vector sum of the time difference
between the picks in units of seconds and of a potential travel time
between the stations in units of seconds:
and
where is the horizontal distance between the sensor locations
of stations in units of km and
is the
clusterSearch.averageVelocity in units of km/s. Activate
use3D for considering 3D distances between sensor
locations. Therefore, and
clusterSearch.maxSearchDist take units of seconds.
As the cluster search is done over time and location, the additional configurable
velocity parameter, clusterSearch.averageVelocity, is required to transform
the input parameters of the cluster search in the same dimension (time).
The velocity is a weighting factor between inter-station distances and
travel-time differences. A starting value should represent the average apparent
horizontal or the total medium P-wave velocity of the crust.
Warning
When the number of buffered cluster origins reaches clusterSearch.maxOrigins,
no more new origins can be formed and warnings are issued. Adjust accordingly:
Limiting in time¶
In real time picks are received in the order of their creation times. They are
considered for clustering if their pick times are within a time window
before the cluster reference time. The time window is defined by
clusterSearch.maxPickDelay but the cluster reference time is defined
either by the
Pick time of the latest pick of the received picks when
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode= ‘LastPick’ (default),Pick time of the latest received pick which defines are group of N picks within
clusterSearch.maxPickDelaywhenclusterSearch.referenceTimeMode= ‘MaxPickDelay’. Here, N is the maximum ofclusterSearch.minSizeandassociation.minPhase. This mode is relevant if only very few stations with significantly different data delay provide the picks. Otherwise picks may not be available for clustering at the same time preventing to form clusters and new origins.
Thus, when setting clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = ‘MaxPickDelay’
re-setting the cluster reference time is delayed depending on the amount and
density of incoming picks. With this option picks which have a larger delay can
be considered. Such delays occur, e.g., due to larger data delays or larger
record lengths.
where
:time at which the pick was made,
: actual time of the phase arrival.
Picks available within a trapezoid-like time window are considered for
clustering.
For a pick with zero delay, the cluster reference time is initially set and picks
within the blue trapezoid (figure below) are considered.
Normally, picks have some delay which delays defining the trapezoid. This makes accessible
other picks available with some delay, too, allowing these picks to be considered
(green trapezoid). Subsequently, the trapezoid is extended until the
cluster reference time is updated.
This may be the next pick with a larger pick time
(olive trapezoid, clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = ‘LastPick’) or
the time of the pick which is preceded by at least clusterSearch.minSize
picks within clusterSearch.maxPickDelay (yellow trapezoid,
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = ‘MinPickDelay’).
Thus, picks which have a long delay do not fall within the relevant trapezoid and
cannot be considered for clustering as they are not available at the time of clustering.
The trapezoid is set with respect to the cluster reference time, CRT1 in the figure below, considering the delay of the defining pick and the time until the next relevant pick which updates the reference time (CRT2):
CRT2 with
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode= ‘LastPick’ orDeleyed CRT2 since
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode= ‘MaxPickDelay’.
The longer the time until the update, the more picks with larger delays can be considered for clustering, e.g., the delayed clustered pick in the figure below.
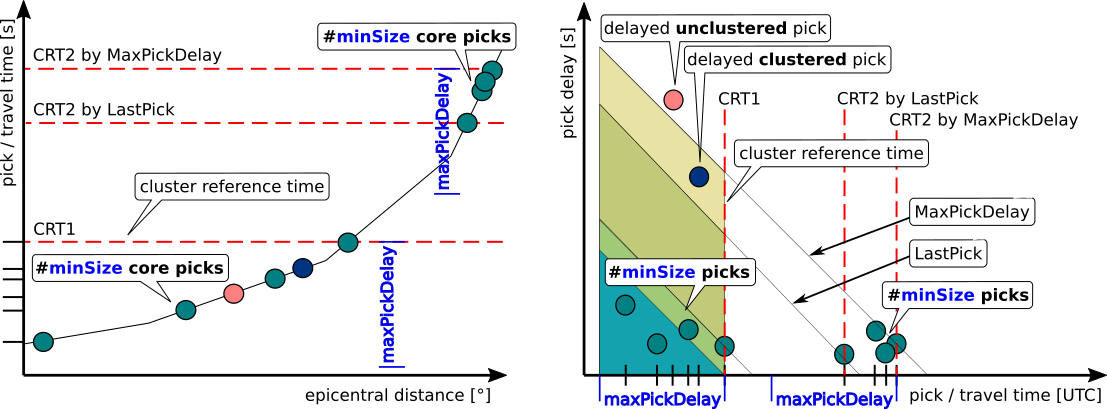
Figure 3: Schematic view of pick time vs. pick delay time of picks for clustering.
The cluster reference time determines the trapezoid within which picks can be
considered for clustering.
Here, the delayed clustered pick only becomes part of the cluster with
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = ‘MaxPickDelay’.¶
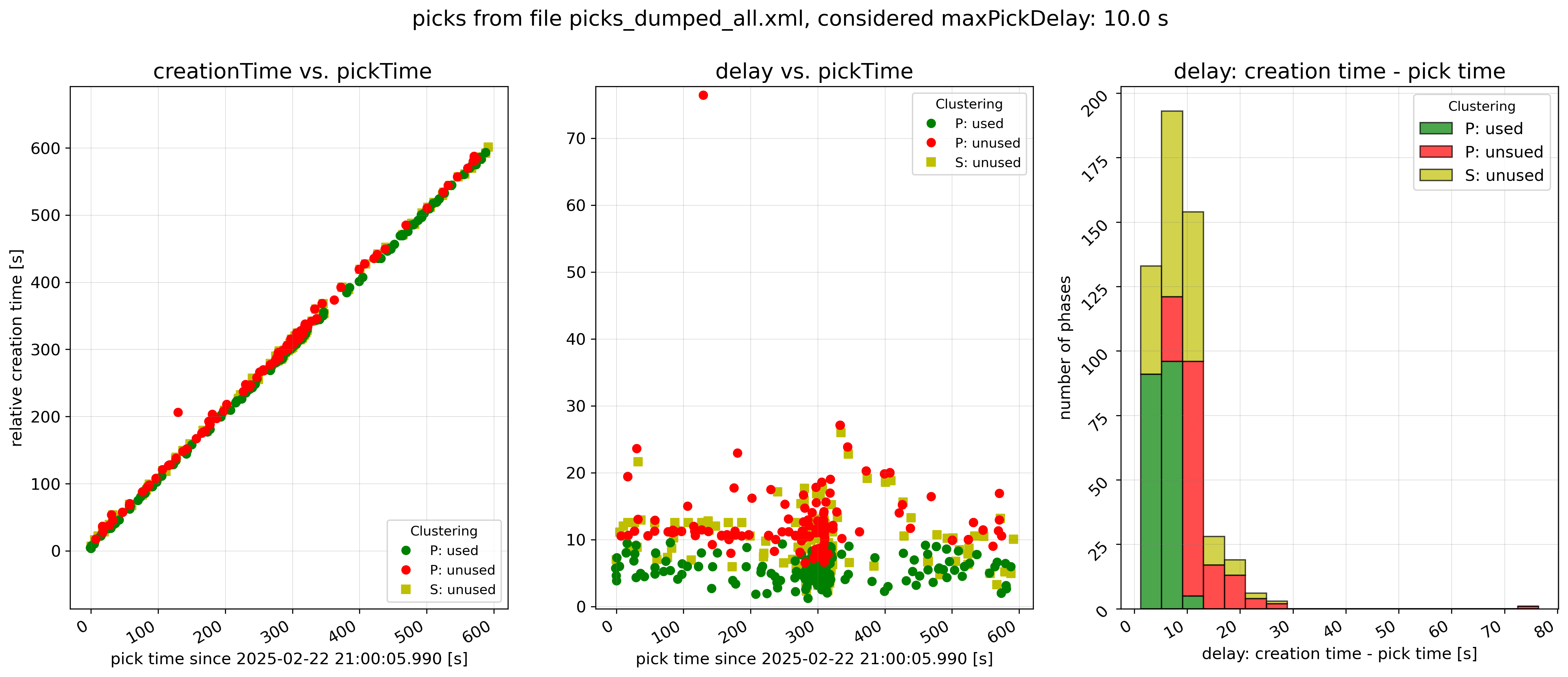
Figure 4: clusterSearch.maxPickDelay = 10 s.¶
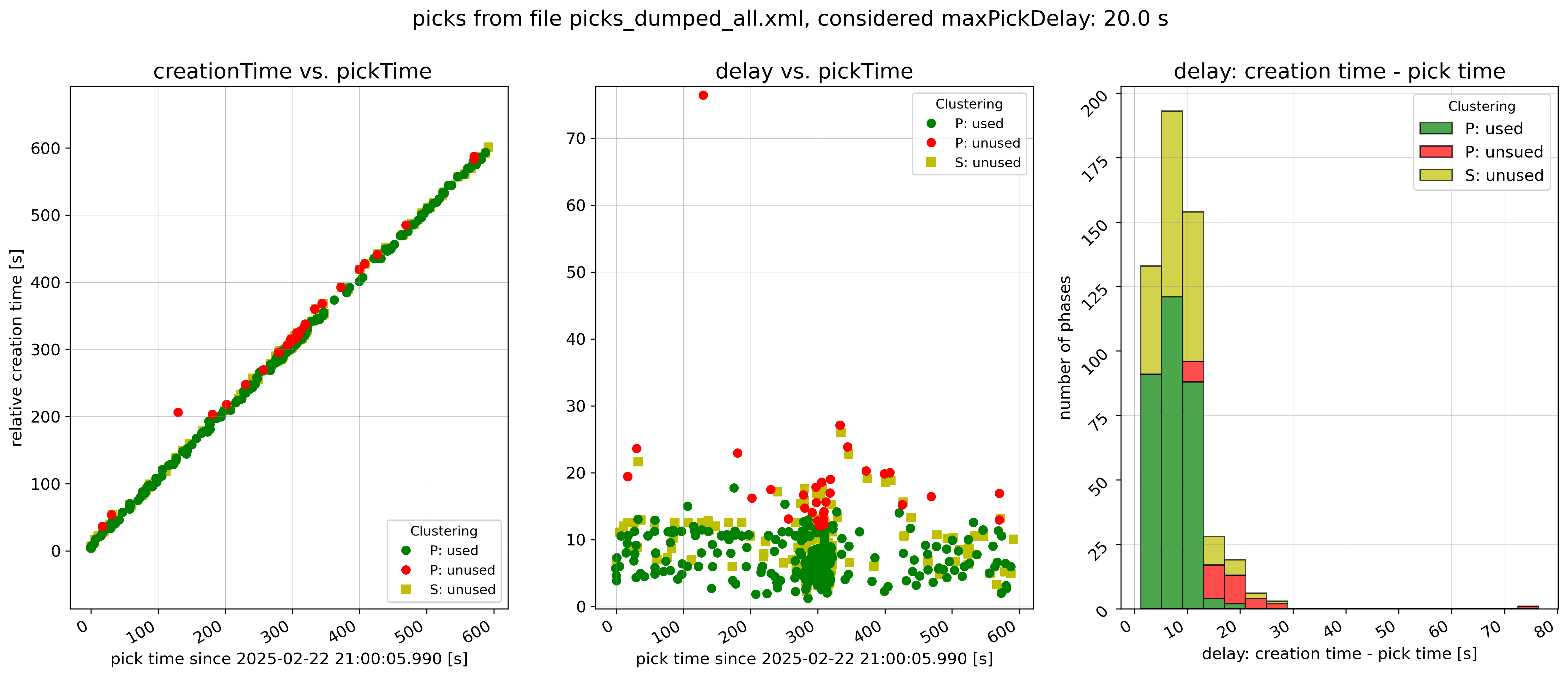
Figure 5: clusterSearch.maxPickDelay = 20 s.
Real-life examples of picks considered for clustering with different values
for clusterSearch.maxPickDelay and
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = ‘MaxPickDelay’. P picks with
green symbols are considered for clustering, picks with red symbols are not.
Clearly, the larger clusterSearch.maxPickDelay the more picks are
available for clustering but the more clusters from unrelated picks (false
clusters) may be created.¶
Note
For small and similar delays of all P picks,
clusterSearch.maxPickDelaycan be directly read from travel-time curves. A small margin should be added account for differences in delay.In XML playbacks, the creation times may not be representative of real-time conditions. Therefore, pick times may be used for the timing instead of creation times. Read the section Real-Time Applications for more details and the consequences.
If picks arrive with a larger delay than others, there is a risk that they cannot
be considered anymore for the cluster. When only few picks are available the events
may then be missed. To overcome the issue, you may increase clusterSearch.maxPickDelay
or set the parameter clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = “MaxPickDelay”.
While increasing clusterSearch.maxPickDelay may slow down the clustering
and increase the risk to cluster unrelated picks,
clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = “MaxPickDelay” will only increase the
cluster reference time if at least clusterSearch.minSize P picks are
available in the considered time window. Run scanloc on the command line
with the --cluster-search-log-file to learn about cluster reference
times and the considered picks. A suggestion for clusterSearch.maxPickDelay
is provided in the summary section at the end of the resulting output. For more
options read the section Tuning and optimization.
Within one cluster, the difference in the pick times between the
cluster reference time and any other pick must thus not exceed clusterSearch.maxPickDelay.
Otherwise the pick is rejected from clustering. The parameter clusterSearch.maxPickDelay
has a big impact on the performance of the cluster search. Choosing the parameter
as small as possible will speed up scanloc and will reduce the complexity of the
cluster search.
The DBSCAN algorithm can deliver multiple pick clusters. The cluster search can
be disabled using clusterSearch.maxPickDelay:
# Maximum allowed difference between P pick and cluster reference time(latest pick time).
# The cluster search ignores all picks which exceed the value. Using "-1" enables all picks
# regardless of the delay. Unit: seconds.
clusterSearch.maxPickDelay = 0
Then, only external origin can be considered for phase association.
In combination with buffer.futureTimeDelta or
--future-time-delta
applying clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode = “MaxPickDelay” may make
updating the cluster reference time more robust to singular data timing issues.
However, the timing issue of the waveforms and the pick times remain and may
impact the clustering itself. Therefore, buffer.futureTimeDelta
should only be configured with positive values only in extraordinary
circumstances.
Limiting in space¶
The cluster search can be constraint to stations within a region given by the
coordinate of a central point and the radius around that point. The region constraint
is configured through clusterSearch.regionFilter. Applying this parameter
will disregard picks from stations outside the region for cluster search increasing
the speed and the complexity. Nevertheless, the excluded picks are available for
phase association.
For running the cluster search in several regions in parallel, different instances of scanloc taking picks from the same of different pickers can be created and started.
Cluster splitting¶
Originally, clusters may contain multiple phase picks from the same sensor but only one pick per sensor shall be accepted. Therefore, the clusters with picks from the same sensor are split into separate clusters with only one pick per sensor.
Typcially, the sensors are discriminated by their sensor location codes, LOC, as
defined in the SEED manual [30] using the NET.STA.LOC.CHA stream
representation. Since some stations provide data for different sensors on the
same sensor location code but with different channel codes (e.g. seismic and
infrasound sensors), the channel code, CHA, may be a better discrimination
measure for sensor identity. On the other hand, picks made on different sensor
location of the same station could be attributed to the same site, e.g., in
regional or telseismic monitoring. Then, the station code, STA, would be
preferred for discrimination. The parameter
clusterSearch.streamCheckLevel allows defining the stream level on
which to check sensor identity.
Hint
In order to consider picks from equal sensor location codes but with different channel IDs, configure scanloc with
clusterSearch.streamCheckLevel = cha
All new clusters are considered new origins. By activating
clusterSearch.checkOrigins, all new clusters are checked again.
Clusters not meeting the configured cluster criteria are removed from the buffer.
The check imposes an additional overhead on the cluster search but it typically
lowers the chance for fake solutions and it also lowers the load on the
phase association and scanloc in general.
Tuning and optimization¶
Use the option --cluster-search-log-file to store detailed information
on the clustering process in a file, e.g., cluster.log. The given values can be
used to optimize the cluster search parameters.
scanloc --ep picks.xml -d [database] --cluster-search-log-file cluster.log > origins.xml
For optimizing the configuration of the parameter clusterSearch.maxPickDelay
use the default value first:
clusterSearch.maxPickDelay = -1
The given output file contains the clusters with the pick details. After each cluster the maximum time interval between the first and the last pick in the cluster is provided. A summary at the end of the file shows the largest value, e.g.:
+ cluster source: -69.6279, -21.4715, 1231891115.191
+ pick ID: *20090113.235827.36-AIC-CX.PB01..HHZ X: -69.4874 Y: -21.0432 time: 1231891107.368 distance: 14.715 s
+ pick ID: 20090113.235832.91-AIC-CX.PB02..HHZ X: -69.8960 Y: -21.3197 time: 1231891112.918 distance: 8.443 s
+ pick ID: 20090113.235839.53-AIC-CX.PB07..HHZ X: -69.8862 Y: -21.7267 time: 1231891119.538 distance: 10.677 s
+ pick ID: 20090113.235840.94-AIC-CX.PB09..HHZ X: -69.2419 Y: -21.7964 time: 1231891120.940 distance: 14.645 s
+ 1 split cluster
+ cluster
+ 20090113.235827.36-AIC-CX.PB01..HHZ
+ 20090113.235832.91-AIC-CX.PB02..HHZ
+ 20090113.235839.53-AIC-CX.PB07..HHZ
+ 20090113.235840.94-AIC-CX.PB09..HHZ
+ maximum pick time interval for this cluster: 13.572 s
+ minimum maxPickDelay required for this cluster: 13.572 s
+ end
+ end
+ end
+ end
+ summary:
+ maximum experienced cluster time interval: 40.840 s
+ minimum value of clusterSearch.maxPickDelay for all clusters: 13.572 s
The summary value can be used as a lower proxy to set
clusterSearch.maxPickDelay.
Locating¶
Clusters are located by the configured locator. If the
location fails, the origin is ignored unless clusterSearch.preliminary
is active. Then, preliminary values are chosen:
Origin location is the center of the detecting stations,
Origin time is the time of the first phase pick,
Status is set to preliminary.
The status will be unset if more phases can be associated and the new origin can be located.
Phase Association¶
When a cluster of P picks meeting association.minPhase is found
or an external origin arrives, scanloc tries
to associates additional P- and S-type phase picks which are
buffered and which meet the association criteria:
P-type picks:
the epicentral distance does not exceed
association.maxDist,no other P pick from the same channel exists in the origin,
the pick time,
, of the new pick is close to the arrival time predicted by the travel-time interface,
, considering
association.maxPResidual:
S-type picks:
the epicentral distance does not exceed
association.maxDist,the evaluation mode of the pick is manual or the pick references a P pick which has been already associated. The reference to a P pick is given as a comment of the S pick. Example:
<pick> ... <comment> <text>Pick/20230726100411.964268.1316601</text> <id>RefPickID</id> </comment> </pick>
The reference check serves as a quality control feature. I can be dropped by
--drop-reference-checkandassociation.dropReferenceCheck.the pick time,
, of the new pick is close to the arrival time predicted by the travel-time interface,
, considering
association.maxSResidual:
The new set of picks are used for relocating.
In case the buffered pick is a P pick the algorithm
directly attempts to associate the pick solely based on the residual. It tries
to relocate
the solution after each successful association. P picks with travel-time
residuals larger than association.maxResidual are rejected.
After the P-picks are associated and relocated, scanloc tries to associate the
S picks. This association is not based
on the residual but on the P pick referenced by the S pick. The S pick is
only associated in case the reference P pick is already associated to the
origin. Also after each S pick a relocation is done. In case the relocation
fails or the event residual is larger than maxRMS,
the S pick is associated with a weight of 0. The score of the resulting
origin is compared with scores of origins belonging to the same event. In case
the score is higher than the rest of the origins, the origin is
sent out.
In addition to origins from the cluster search, scanloc can also treat external origins that are created by other associators, e.g., scautoloc [15]. In case an such origin is received scanloc tries to associate all picks in the buffer to the origin. The association and the following processes are the same as described above. See figure Simplified work flow of scanloc. for an overview.
The maximum epicentral distance up to which picks are considered is configured
by association.maxDist. However, this parameter can be overruled per
network and station by providing a station table in a file given by
association.stationConfig. As in scautoloc [15] each line of the
table consists of the network code, the station code, a switch and the maximum
epicentral distance in degrees. Wildcards can be used for the network and the
station code. The switch causes the associator to consider (=1) or to ignore
(=0) a network or a station.
The last occurrence of an item in a table overrules previous ones, e.g.
* * 1 180
GR * 1 60
GR GRA1 1 20
Z3 * 0 180
For associating the picks, travel times from look-up tables are used. The
association.tableType and the association.table can be
configured to provide specific tables which may be more appropriate for specific
regions. Currently, only a limited number of travel-time table types
(association.tableType) are supported. scanloc provides
densely-sampled travel-time tables for LOCSAT.
types supported by association.tableType |
location of tables for association.table |
|---|---|
homogeneous |
model is defined by |
libtau |
@DATADIR@/ttt |
LOCSAT |
@DATADIR@/locsat/tables, tables should not be modified |
Travel times from other sources can be considered by a plugin exposing the travel times to the travel-time interface. The considered table must provide the time for all considered phases.
Example configuration (scanloc.cfg):
# Type of travel-time tables for phase association. May be different from locator.
# Use e.g. libtau or LOCSAT.
association.tableType = LOCSAT
# Name of travel-time table used for phase association. May be different from locator
# profile.
association.table = iasp91_scanloc
Note
Travel-time tables used during association and location may be different.
Therefore the travel-time residuals visible after relocating may be different
from the travel-time residuals considered during association.
The differences must be considered when configuring association.maxPResidual
and association.maxSResidual.
Processing external origins¶
Origins received from other modules through the messaging or provided by XML files
can be processed and more phases can be associated. In
order to ignore such external origins set buffer.ignoreOrigins:
buffer.ignoreOrigins = true
Processing of external origins may be undesired when
Involving other modules excepting origins by the messaging system, e.g., screloc [26]. These modules may run in a loop with scanloc.
Receiving origins from other systems.
Configure buffer.authorWhiteList with the author names of
origins which shall be processed, e.g., scautoloc [15]:
buffer.authorWhiteList = scautoloc@localhost
Automatic and manual origins from all other authors will be ignored.
Status of origins¶
The status of origins can be set during pick processing
Normally, the status of origins is unset.
The status of origins from cluster search which only be located with fixed depth (
fixDepth,forceFixDepth) is set to preliminary.The status of origins which can be relocated with a free-depth solution is set to unset if the origin status of the origin was previously set.
However, the evaluation status may be later changed at different times by different modules, e.g., the gempa module sceval. In order to track this history a journal entry is created and sent when running scanloc with a connection to the messaging or added to the XML output long with the origins. In future versions of SeisComP such journal entries will be made accessible in scolv.
Sending of origins¶
Before sending a new internal origin to the
messaging or to XML output (--ep) it is tested against the
configuration:
Picks are removed when their travel-time residual >
association.maxResidualand origins are relocated,Origins are skipped when the score <
minScore,Origins are skipped when the depth >
ignoreDepth.
The remaining internal origins are evaluated based on scoring.
The best origin of the same internal event is the one
which has the highest score. When meeting the parameters
ignoreDepth, maxRMS and minScore it is sent to the
SeisComP messaging [11] or to stdout in case of non-real-time playbacks
(--ep).
In real-time operation, the sending of origins may be delayed allowing to find
new origins with higher score.
The delay reduces the amount of origins in SeisComP systems and the load of
other modules. The send interval is controlled by the publication
configuration parameters.
Note
In non-real-time (--ep) playbacks, the publication
configuration parameters are ignored and all origins are sent without delay.
Performance considerations¶
In case of dense large-N networks and high seismicity situations,
very many phase picks, e.g., hundreds of picks for a single event may be
provided to and processed by scanloc. In such situations, scanloc was observed
to slow down with default parameters but a sensible configuration of
clusterSearch.maxSize and association.arrivalCountMinRes
could overcome the obstacles.
- clusterSearch.maxSize controls the maximum number of picks in a cluster
after selecting core points and before adding more picks. Since core points are first collected, clusters may have a higher number of picks. The goal of this parameter is to speed up scanloc. The parameter may help to increase the performance of scanloc in case of dense large-N networks where very many cluster can be formed due to the proximity of stations or generous configuration.
association.arrivalCountMinRes controls the association of picks to origins. For origins with a larger number of arrivals than configured, the association of P and S picks is controlled by the minimum of (association.maxPResidual, association.maxResidual) and (association.maxSResidual, association.maxResidual), respectively. The goal of this parameter is to speed up scanloc by only associating picks to already stable origins defined by many arrivals where new picks later on are unlikely to be removed again from origins by residual checks. The parameter may help to increase the performance of scanloc in case of dense large-N networks where very stations provide phase picks.
Internal Origins and Events¶
scanloc forms
Internal origins from the locations and the associated picks (arrivals) of new arrival sets,
Internal events from internal origins based on the
eventAssociation.*parameters. The procedure is similar to scevent [20]. An origin is compared to the preferred origin of an existing internal event. It is associated to the existing internal event if one of the criteria applies:the origins share a minimum of
eventAssociation.minMatchingArrivalsarrivals. Arrivals must be identical by the ID of the referenced pick unlesseventAssociation.compareAllArrivalTimes= true. Then, a margin ofeventAssociation.maxMatchingArrivalTimeDiffapplies for considering different picks to be the same.the differences in origin time AND epicenter is within
eventAssociation.maxTimeSpanANDeventAssociation.maxDist, respectively.
Only if the score of a new origin exceeds the score of the last sent origin of the same internal event, the new origin is sent out.
Locating Origins¶
scanloc locates internal origins based on the configuration by the
locator.type and locator.profile parameters. The list of
available locators can be printed by scanloc:
scanloc --locator-list
In order to make an alternative locator available to scanloc, the respective plugin must be loaded.
Consider a fast locator (locator.type), e.g., LOCSAT or
Hypo71 [3] with an appropriate profile (locator.profile).
For LOCSAT dense the provided dense travel-time tables may
be more appropriate at short epicentral distance than the default one.
Example configuration (scanloc.cfg):
# The locator type to use
locator.type = LOCSAT
# The locator profile to use
locator.profile = iasp91_scanloc
Note
Computational speed can be an issue when alternative locators are used and when many picks are to be tested during association. In this case scanloc can be configured with LOCSAT [5] but screloc [26] may be used along with the preferred locator and profile to relocate the origin. The locator NonLinLoc [35] is certainly too slow for being used in scanloc but is a good option for screloc.
If the locator fails to locate and locator.fixDepth is active, the
hypocenter depth is fixed to defaultDepth and the origin is relocated.
Scoring Origins¶
Each internal origin is evaluated and ranked by
calculating a in order for scanloc to define the preferred origin
of an internal event and for comparison against
minScore before
eventually sending an origin.
The score is calculated by a score processor which is provided by a plugin. Score plugins shipped with scanloc can be equally applied to scanloc and scevent [20]. The plugins currently provided along with scanloc are:
scoresum (default): OriginSum calculating the score as a weighted sum of Origin attributes.
scoremf: OriginMultiFeature calculating the score as a weighted sum of Origin attributes like in OriginSum but allowing to add additional contributions by picks from infrasound, strong motion and low-gain instruments, authors, gap, etc.
but more processors can be implemented by gempa or anyone else. Read the section Plugin development for the details.
OriginSum¶
The OriginSum score processor is provided by the plugin scoresum located in
@DATADIR@/plugins/scevent/scoresum.so. The plugin calculates the
for origins as a weighted sum from
The number of associated and used P- (Is-) and S-phase picks considering separately the number of used pick times, slowness and backazimuth (pTimeCount, pSloCount, pBazCount and sTimeCount, sSloCount, sBazCount),
The number of loosely associated P and S picks (p0Count and s0Count). Such picks are arrivals with 0 weight. They are not used at all for origin location,
Source depth represented by depthFactor (see below) and
RMS time residual represented by residualFactor (see below).
Methodology¶
The score is computed as
with
where the weight factors score.sum.p [0:2], score.sum.p0 ,
score.sum.s [0:2], score.sum.s0 ,
score.sum.depth and score.sum.residual can be configured.
The values for depthFactor and residualFactor are derived from origin
depth and time residual and the configured values for
score.sum.normalizationDepth and score.sum.normalizationRMS.
Higher weight is given to origins with shallower depth. You may set
score.sum.depth to form the score independent of depth in regions with
shallow and deep seismicity:
score.sum.depth = 0
Phase picks may not only provide measurements of time but also of slowness
and back azimuth. The existence of these additional values, if used by the
locator, may impact the solution quality which can be considered by the score.
If you believe that slowness and back azimuth may provide valuable information,
the contribution to score by these picks may be increased by configuring
score.sum.p and score.sum.s with additional weights for slowness
and backazimuth like
score.sum.p = 1,0.5,0.5
score.sum.s = 1,0.5,0.5
Read the documentation of the locators in SeisComP in order to understand if slowness and back azimuth are considered. An overview over locators is given in the concepts section of the SeisComP documentation [6].
Configuration¶
For utilizing the scorsum plugin with the OriginSum score processor in scanloc configure scanloc as:
plugins = ${plugins},scoresum
score = OriginSum
For utilizing the scoresum plugin with the OriginSum score processor in scevent configure scevent as:
plugins = ${plugins},scoresum
eventAssociation.score = OriginSum
eventAssociation.priorities = ...,SCORE,...
OriginMultiFeature¶
The OriginMultiFeature score processor is provided by the plugin scoremf
located in @DATADIR@/plugins/scevent/scoremf.so. The plugin calculates
the for origins similar to
OriginSum but allowing to add additional
contributions by picks from infrasound, strong motion and low-gain instruments,
authors, azimuthal gap, etc.
Methodology¶
The score is computed as
with
However, when origin time residual or depth exceed
score.mf.weights.normalizationRMS and
score.mf.weights.normalizationDepth, respectively, then
which typically assigns a very low priority to an origin.
Phase picks may not only provide measurements of time but also of slowness
and back azimuth. The existence of these additional values, if used by the
locator, may impact the solution quality which can be considered by the score.
If you believe that slowness and back azimuth may provide valuable information,
the contribution to score by these picks may be increased by configuring
score.sum.p with weights for slowness and backazimuth like
score.mf.weights.p = 1,0.5,0.5
Note
All elements in the equations above starting with score.mf. are configurable parameters. Read the section ScoreMF plugin for the full description of parameters.
Configuration¶
For utilizing the scoremf plugin with the OriginMultiFeature score processor
in scanloc configure scanloc as (scanloc.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins},scoremf
score = OriginMultiFeature
For utilizing the scoremf plugin with the OriginMultiFeature score processor
in scevent [20] configure scevent as (scevent.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins},scoremf
eventAssociation.score = OriginMultiFeature
eventAssociation.priorities = ...,SCORE,...
Plugin development¶
Custom score processors may be implemented by additional plugins. You may develop such plugins yourself or request a development from gempa GmbH. An introduction into the development is given on: GitHub .
For utilizing the pluginName plugin with the processorName processor in
scanloc configure scanloc as (scanloc.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins},scoresum
score = OriginSum
For utilizing the pluginName plugin with the processorName processor in
scevent [20] configure scevent as (scevent.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins},pluginName
eventAssociation.score = processorName
eventAssociation.priorities = ...,SCORE,...
Hint
When located in @DATADIR@/plugins/scevent, both scanloc and
scevent [20] can access the plugins as realized also with scoresum and
scoremf.
Pipeline Systems¶
When operating scanloc in a pipeline, configure connection.subscriptions
to receive picks and origins from and connection.primaryGroup to send
origins to the right message group.
Alternatively you may configure buffer.authorWhiteList for receiving
picks and origins from modules with the listed authors. In this case, configuring
new message groups for receiving and sending objects may not be required depending
on the other modules involved in the pipeline.
Please also understand the note on public IDs of the buffer section.
Redundant Systems¶
In redundant systems where origins are received from other machines with idential or simialar setup you may wish to suppress re-processing these origins. Read section Processing external origins for the configuration.
Association of Teleseismic Phases¶
Dense local networks used to monitor local seismicity are often able to catch also a significant number of phases from earthquakes at teleseismic distances. Such phases include Pdiff or PKP. Especially PKP may contain a significant amount of energy at higher frequencies. Therefore PKP is often detected by networks that are tuned to detect local earthquakes. Due to the steep incidence and the low horizontal slowness of these phases, they are sometimes located as fake deep earthquakes below the network. scanloc can be used to suppress this type of fake events.
In a 2-pipeline setup, scanloc can associate such teleseismic phases recorded by the local network with origins that were found by the pipeline for monitoring teleseismic earthquakes. Then scevent [20] will associate the origins from the teleseismic pipeline with the fake origins from the pipeline for local monitoring to the same event. The assumption is that the origins from the teleseismic pipeline win over the origins from pipeline for local monitoring because they have more associated arrivals. In this case the origins from pipeline for teleseismic monitoring that has most phases becomes the preferred origin for the event. This scanloc feature requires an extended license.
Setup of a 2-pipeline system
Generate a 2-pipeline system involving at least scautopick [16], scanloc and scevent [20] :
Pipeline 1 monitors teleseismic earthquakes using scautopick, scautoloc, scanloc and default message groups.
Pipeline 2 monitors local earthquakes using l1autopick, l1autoloc and l1scanloc using the message groups L1PICK and L1LOCATION.
Let scanloc not perform cluster search (
clusterSearch.maxOrigins= 0) but allow scanloc to only associate P picks from pipelines 2 based on origins from scautoloc (connection.subscriptions = “LOCATION, L1PICK” in the global module parameters). Configure scanloc to associate the picks from pipeline 2 as picks with zero weight when they are, e.g., in the PKP or Pdiff distance range. Use one zeroWeight profiles per phase.In order to facilitate association of teleseismic picks, the picks and the origins must be kept in memory for sufficient time. Increase
buffer.pickKeepandbuffer.originKeepaccordingly, e.g., to 1800 s.In this way zero-weight picks will not be used for locating the event but are part of the origin and can be considered by scevent.
Configure scevent to listen to the message groups from both pipelines (e.g. LOCATION and L1LOCATION) and activate the scevent module parameter eventAssociation.allowLooseAssociatedArrivals (
scevent.cfg).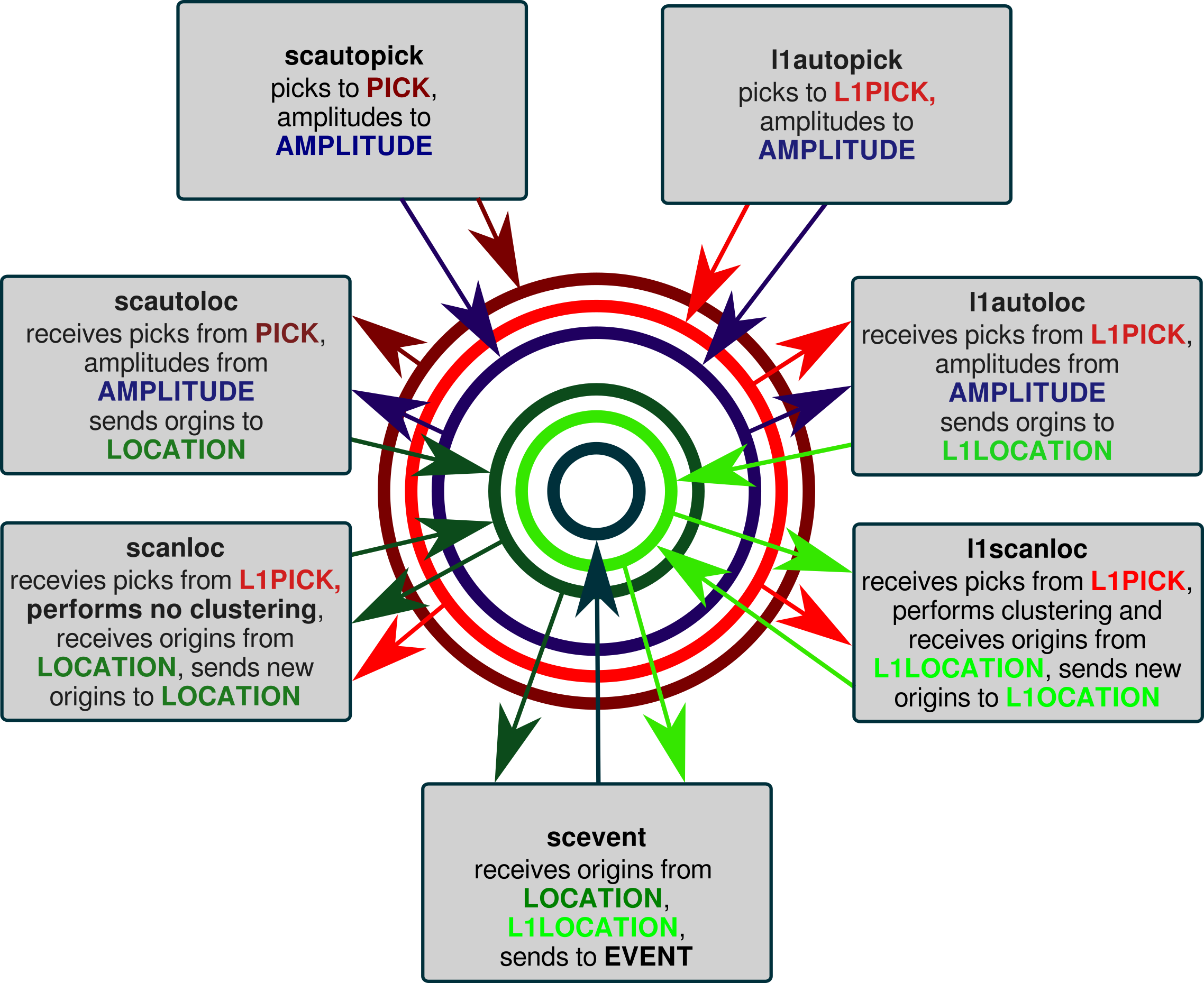
Figure 6: Parameter exchange in a 2-pipeline system. The messaging system, responsible for the parameter exchange, is representated by the circles, indicating the message groups. Teleseismic monitoring is configured with scautopick, scanloc, scautoloc and local monitoring with l1autopick, l1scanloc, l1autoloc.¶
Playback using picks and amplitudes from 2-pipeline system (real-event examples)
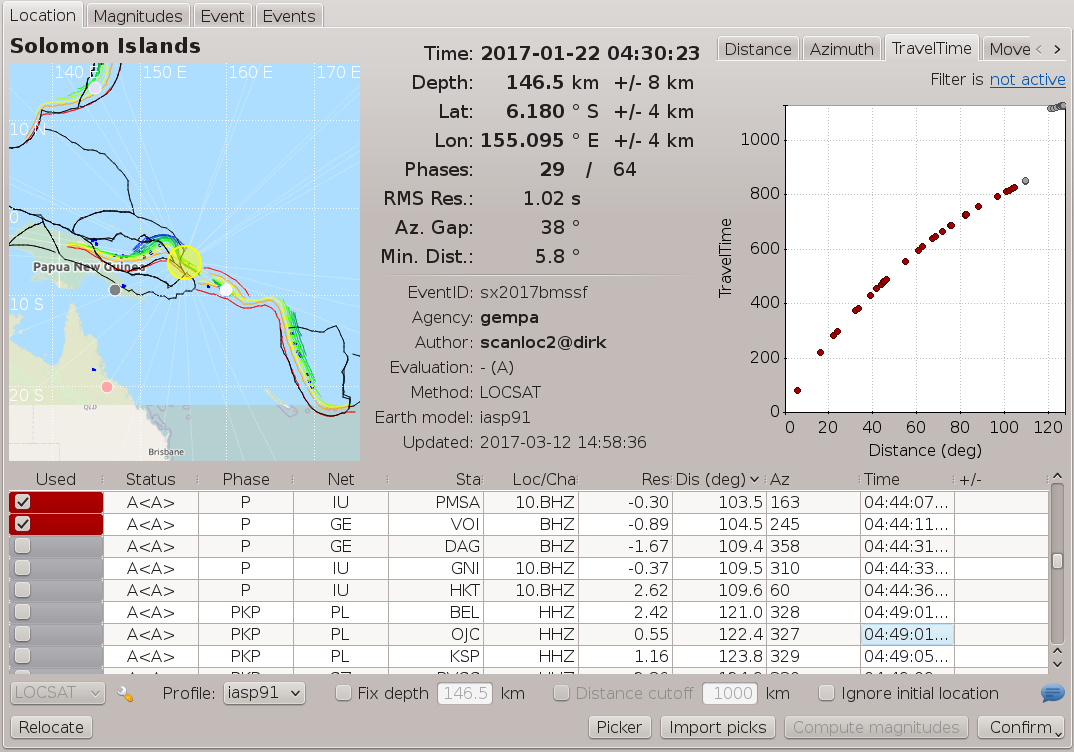
Figure 7: Location tab in scolv with zero-weight picks associated by scanloc as PKP phases.¶
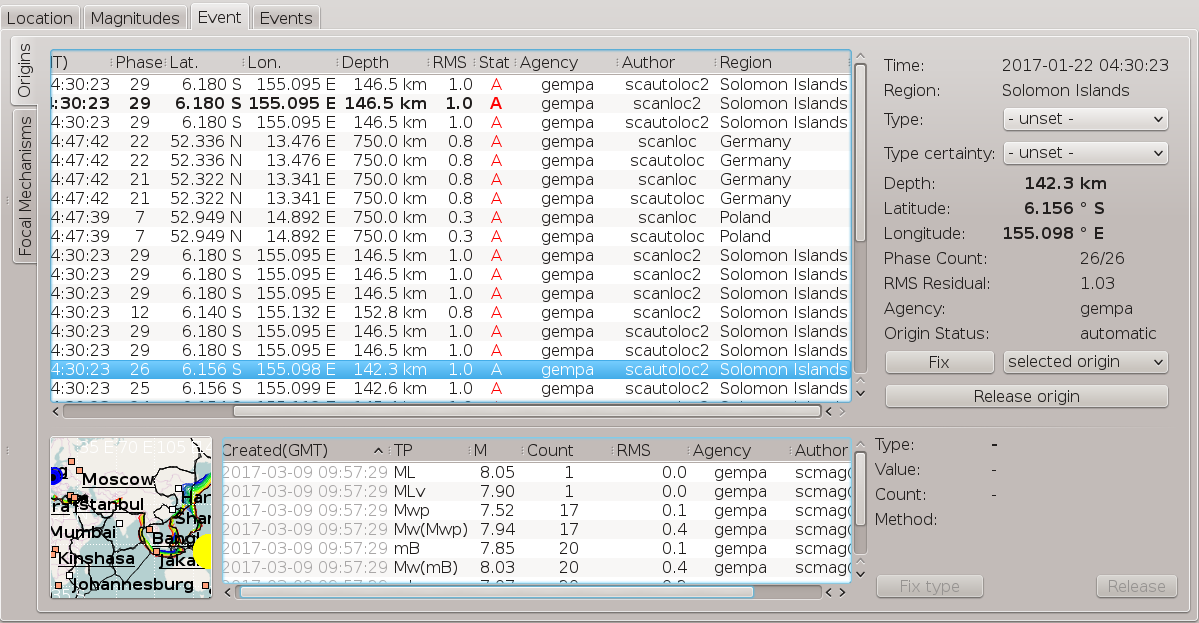
Figure 8: Event tab in scolv showing the origins from the pipelines for local and teleseismic monitoring. The preferred origin located near the Solomon Islands is shown in bold on top. Fake origins in Europe located by pipeline for local monitoring based on PKP phases falsely considered P phases are associated to the event but do not form the preferred origin at any time.¶
Real-Time Applications¶
Run scanloc during real-time processing:
seiscomp start scanloc
Run scanloc on the command line for real-time processing or message-based playbacks with debugging output:
scanloc --debug
Playbacks¶
Playbacks are used to process waveforms or other data on demand as in real time or non-real time, with or without connection to the SeisComP messaging. Objects like picks and origins may be provided to scanloc by XML files or through the messaging.
In playbacks of picks in XML files the performance of scanloc may differ from real-time operation based on messaging:
In real-time operation, the picks are made e.g., by scautopick at some time and considered by scanloc according to their creation times. Delayed picks may become irrelevant for the processing. Configure
buffer.pickKeepandbuffer.originKeepaccordingly.However, the creation times of picks and origins may be obscured when created in a non-real-time playback or manually. Objects from non-real-time playbacks may have almost identical creation times independent of their object times (pick time, origin time, etc.).
In message-based playbacks, picks and origins are provided to scanloc via the messaging system. When created in real time, the creation times of these objects form a realistic time reference for scanloc and should therefore considered using
--timing.In non-real-time XML playbacks (
--ep), scanloc considers picks and origins by default according to their actual times. For objects created in a non-real-time playback object times are most reasonable as creation time is not a valid time reference anymore. However, referencing to object time may result in a behavior which is different from real-time conditions.Therefore, for mimicking real-time conditions in playbacks of objects obtained in real-time conditions consider the command-line option
--timingwith creationTime.
Real-time playbacks¶
Message-based real-time playbacks are useful to test the behavior of scanloc in real time based on objects like Picks, Origins and/or Amplitudes generated before by picking/processing:
Real time where the order of the objects is represented by their creation time.
Non-real time, e.g. manually or by playbacks at high speed. In these cases creation time is not a useful measure of the timing in real time.
Real-time playbacks are supported by auxiliary scripts shipped with the scanloc package.
Objects from real-time picking/processing: Obtain phase picks and origins obtained in real-time and play them back using dump_picks. Amplitudes are useful if other modules such as scautoloc [15], scamp [13] or scmag [23] are involved as well.
Procedure:
Read picks, origins and amplitudes from the database and store them as SCML in a file,
picks.xml, for later playbacks. Additional command-line options may be used to confine the retrieval:dump_picks -d [database] -t "2022-04-01 08:00:00.00~2022-04-01 08:05:00.00" -o objects.xml
Play back all objects sending them to the SeisComP messaging. Start scanloc separately for debugging on the command line considering default timing by creation time of all objects. When done, send all objects to the messaging by playback_picks:
seiscomp stop seiscomp start scmaster scamp scmag scevent scanloc --debug playback_picks picks.xml
Picks from playbacks: Play back picks and amplitudes created by a non-real-time playback possibly in different pipeline [12] sending them to the SeisComP messaging.
Picks and amplitudes are created in playbacks by scautoloc [15] and stored in XML files (SCML format).
Picks and amplitudes are sent specifically to the message groups PICK, L1PICK and AMPLITUDE.
scanloc and l1scanloc listen to picks from PICK and L1PICKS, respectively.
scautoloc [15] additionally needs the pick amplitudes from the subscribed amplitude groups.
Procedure:
Create the XML files by scautopick [16] including picks and amplitudes in a non-real-time playback by the modules as in your 2-pipeline system. Since picks and amplitudes are created by the playback, their creation times are not a relevant measure of the order in which they were created.
scautopick -d [database] --ep --playback -I [your_waveforms] > picks.xml l1autopick -d [database] --ep --playback -I [your_waveforms] > l1picks.xml
Start all required modules including the scanloc instances
seiscomp start scmaster scamp scmag scevent scautoloc l1autoloc scanloc l1scanloc
Execute playback_picks with
--timing pickTimefor sending the picks and amplitudes created by different pickers at different times. Consider timing by pick time of the picks:--timing pickTimeis used as an approixmation of the timing since creation time is not meaningful in this XML playback.playback_picks picks.xml:PICK:AMPLITUDE l1picks.xml:L1PICK:AMPLITUDE --timing pickTime
Non-real-time playbacks¶
Non-real-time (--ep) playbacks are used for very fast processing of
picks and origins which are provided in XML files (SCML format).
The objects were generated before in
Real time and read from the database e.g., by dump_picks or
By non-real-time playbacks, e.g., involving scautopick [16].
In such playbacks, all objects are provided to scanloc
in an XML file with the option --ep.
scanloc writes the results in SCML to stdout which can be re-directed
into another file for further processing.
Note
Execute scanloc always with the appropriate timing.
When picks are created in a non-real-time playback use scanloc with timing
by pick time corresponding to --timing pickTime which is the default in
playbacks. For picks obtained
in real time you should use scanloc with the command-line option
--timing creationTime for setting the timing to creation time.
Play back picks stored in XML format to locate events and to determined the magnitude. Intermediate results are stored in XML files. Inventory and bindings configuration are read from the database. The playback is independent of the messaging. Execute scanloc with the appropriate timing.
Procedure:
Run the playback
scautopick -d [database] --ep --playback -I [your_waveforms]> picks.xml scanloc -d [database] --ep picks.xml --timing [timing] > origins.xml scamp -d [database] --ep origins.xml -I [your_waveforms] > amps.xml scmag -d [database] --ep amps.xml > mags.xml scevent -d [database] --ep mags.xml > events.xml
You may jointly process picks from multiple instances of phase detectors which are executed first. The picks and origins are provided to scanloc after merging the XML files. Example:
scautopick -d [database] --ep --playback -I [your_waveforms] > picks_sp.xml dlpick -d [database] --ep --playback -I [your_waveforms] > picks_dl.xml ccloc -d [database] --offline --ep -I [your_waveforms] > picks_origins_ccloc.xml autothor -d [database] --offline --ep -I [your_waveforms] > picks_origins_autothor.xml scxmlmerge picks_sp.xml picks_dl.xml picks_origins_ccloc.xml picks_origins_autothor.xml > objects.xml scanloc -d [database] --ep objects.xml --timing [timing] > origins.xml scamp -d [database] --ep origins.xml -I [your_waveforms] > amps.xml scmag -d [database] --ep amps.xml > mags.xml scevent -d [database] --ep mags.xml > events.xml
Enter the results into the SeisComP system. Either:
Preferred: Events may exist in the database. Update existing events by associating new origins or create new events. Run the messaging system and all modules that shall process the new parameters, e.g. scamp [13], scmag [23] , scevent [20]. Use scdispatch [18] to send the new objects to the messaging system.
seiscomp start scmaster scamp scmag scevent scdispatch -H host -i mags.xml
Instead of the
mags.xml, other parameters created by the playback may be dispatched, e.g., fromorigins.xml. Use scdispatch [18] with -e to ultimately prevent sending event objects.Events do not exist in the database, use scdb [17] to populate the database with all events in
events.xml.scdb -i events.xml -d [database]
Warning
Using scdb [17] for writing event information to the database may result in duplicates if the provided parameters, e.g., events, exist already with another ID. In this case use scdispatch [18] with
mags.xmland running scmaster [24] and scevent [20] instead of scdb [17]. However, scdispatch in newer versions of SeisComP allows ignoring Event objects with the option-e. Then, alsoevents.xmlcan be dispatched.
Play back picks stored in XML format, without a database but inventory and bindings in SCML and with a local file for module configuration.
Procedure:
Set up a local module configuration file, e.g.,
scanloc.cfgcontaining all parameters includingpluginsandcore.plugins. The configuration file is then defined by--config-filereplacing all other module configuration.When using
--config-file, all module configuration including global and default parameters are exclusively read from the given file. Essential plugins for database connection and origin scoring must therefore be defined explicitly bypluginswithin that file or by the command-line option--plugins. Examples:plugins = dbmysql,scoresum,scoremf plugins = dbpostgresql,scoresum
scanloc --plugins dbmysql,scoresum ...
Store the station inventory and the binding configuration from a database in SCML:
scxmldump -d [database] -fI -o inventory.xml scxmldump -d [database] -fC -o config.xml
Continue with the examples above replacing the database option
--databasewith--inventory-db,--config-dband--config-filefor adding the module configuration inscanloc.cfg. Set the timing accordingly:scanloc --inventory-db inventory.xml --config-db config.xml \ --ep picks.xml --timing [timing] \ --config-file scanloc.cfg > origins.xml
Module Configuration¶
etc/defaults/global.cfgetc/defaults/scanloc.cfgetc/global.cfgetc/scanloc.cfg~/.seiscomp/global.cfg~/.seiscomp/scanloc.cfgscanloc inherits global options.
Note
Modules/plugins may require a license file. The default path to license
files is @DATADIR@/licenses/ which can be overridden by global
configuration of the parameter gempa.licensePath. Example:
gempa.licensePath = @CONFIGDIR@/licenses
- defaultDepth¶
Default:
0.0Unit: km
Type: double
Default source depth used for locating origins. The range of supported values depends on the configured travel-time interface and locator.
When origin depth after locating is 0.0 or undefined, the depth is corrected to "defaultDepth" without relocating since the situation indicates issues.
Note: A similar parameter may require configuration for score plugins.
- ignoreDepth¶
Default:
650.0Unit: km
Type: double
Maximum depth of an origin to be sent.
Note: A similar parameter may require configuration for score plugins.
- use3D¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Compute distances in 3D for cluster search, phase association and internal event association. Otherwise, distances are measured from geographic coordinates ignoring elevation.
- maxRMS¶
Default:
1.5Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed overall residual of an origin to be sent.
- minScore¶
Default:
0.0Type: double
Minimum score of an origin to be sent.
- score¶
Default:
OriginSumType: string
Values:
OriginSum,OriginMultiFeatureDefines the score processor to be used for ranking origins of events. Additional configuration of the plugin and the plugin parameters is required.
- pickComparisonLevel¶
Default:
locType: string
Values:
sta,loc,chaThe level up to which compare stream IDs of multiple picks in order to avoid origins with multiple picks from identical stream level, e.g., station (sta), sensor location (loc) or channel (cha).
The level is derived from the NET.STA.LOC.CHA stream representation. Picks with equal stream IDs on the given level are treated as originating from the same stream no matter of the ID on a lower level. Clusters having picks on streams equal on the given level are split into new clusters with unique streams. During association picks equal on the given level are ignored - the first assigned pick is considered.
Note
buffer.* Define buffering of picks and origins. scanloc only treats picks and origins kept in the buffer.
- buffer.pickKeep¶
Default:
180.0Unit: s
Type: double
Time to keep picks. Time comparison is based on the pick times. In non-real time playbacks the time to keep picks is usually compressed.
- buffer.pickIgnoreStreamID¶
Type: list:string
Ignore picks created on given stream ID(s). Stream IDs may contain wildcards. Separate multiple IDs by comma.
- buffer.ignorePickTimeDifference¶
Default:
0.0Unit: s
Type: double
Generally, all available picks are added to the buffer and made available for processing. Use this option to ignore new picks made on the same data stream within the given time difference to a previously buffered pick. A value of 0.0 s ignores all picks with identical times.
- buffer.originKeep¶
Default:
180.0Unit: s
Type: double
Time to keep origins. Time comparison is based on the origin times. In non-real time playbacks the time to keep orgins is usually compressed.
- buffer.ignoreOrigins¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Ignore and do not buffer external origins received from messaging or from XML files.
Default: Accept external origins from messaging or XML and associate more phases.
- buffer.ignoreManualOrigins¶
Default:
trueType: boolean
Ignore and do not buffer manual external origins received from messaging or from XML files.
The parameter "buffer.ignoreOrigins" must be inactive for this option to be effective.
- buffer.originStatusIgnore¶
Type: list:string
Values:
rejected,reported,preliminary,confirmed,reviewed,finalIgnore an external origin if its status has any of the given states. The option is ignored for manual origins if buffer.ignoreManualOrigins = false.
- buffer.authorWhiteList¶
Type: list:string
Only buffer picks or origins from the given authors. Separate multiple authors by comma. Picks and origins from other authors will be ignored. Wildcards are supported. This parameter overrides "buffer.originAuthorWhiteList". Manual origins are treated regardless of the author as defined by "buffer.ignoreManualOrigins". The parameter allows operation of scanloc based on picks and origins from a specific module, e.g., in a pipeline.
- buffer.originAuthorWhiteList¶
Type: list:string
Deprecated parameter which will be removed in 2025. Use "buffer.authorWhiteList" instead which overrides this parameter!
Only buffer external origins from the given authors to the. Separate multiple authors by comma. Manual origins are treated regardless of the author as defined by "buffer.ignoreManualOrigins".
The parameter "buffer.ignoreOrigins" must be inactive for this option to be effective.
- buffer.futureTimeDelta¶
Default:
0.0Unit: s
Type: double
The time delta to the future. Positive values allow objects with times in the future to be buffered when the difference to current time or to creation time is not larger than the given value.
Normally, objects like picks and origins are created after their actual times and all other objects are spurious and should be ignored. In case of wrong sensor timing or faster-than-real-time waveform playbacks, objects may be generated with actual times (pick time or origin time) in the future.
If less or equal to 0.0, then all objects created before time of the object or with object times in the future are ignored.
Note
clusterSearch.* Parameters controlling the cluster search based on phase picks of configured phase type.
- clusterSearch.phaseType¶
Default:
PType: string
Phase type of considered picks. Valid types: P or Is.
- clusterSearch.minSize¶
Default:
4Type: int
Minimum number of core points (picks) to form a cluster.
- clusterSearch.maxSize¶
Default:
-1Type: int
Maximum number of picks in a cluster when stopping clustering. Eventual clusters may still be larger from core points. Using values < 0 deactivates the feature.
The parameter is meant to support large-N networks where the high network density results in very many clusters with high computational load effectively slowing down the processing of picks. Using reasonable values such as 10 or 15 will reduce the number of clusters while maintaining high quality initial origins.
- clusterSearch.maxPickDelay¶
Default:
-1.0Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed difference between considered picks and cluster reference time (latest pick time). Optimum values can be derived from travel times.The cluster search ignores all picks which exceed the value. Using "-1" enables all picks regardless of the delay.
- clusterSearch.referenceTimeMode¶
Default:
LastPickType: string
Values:
LastPick,MaxPickDelayMode to set the cluster reference time. Read the documentation for the details. Available modes:
LastPick: The pick time of the last incoming P pick is the cluster reference time.
MaxPickDelay: Setting the cluster reference time is delayed until clusterSearch.minSize and association.minPhase picks are available.
- clusterSearch.regionFilter¶
Type: list:double
Cluster only picks which sensor locations are inside the defined region. The region is defined by latitude, longitude and a radius in km. By default the region filter is disabled.
Example: 50.1,12.3,20
- clusterSearch.averageVelocity¶
Default:
7.0Unit: km/s
Type: double
Average velocity used for distance calculation.
- clusterSearch.maxSearchDist¶
Default:
60Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed distance over all core points and maximum allowed distance for neighborhood search. Both account for travel-time difference, inter-station distance and the configured averageVelocity.
- clusterSearch.maxOrigins¶
Default:
128Type: uint
Maximum allowed origins derived from cluster search. Set this option to zero to disable the cluster search completely.
- clusterSearch.preliminary¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Send origins based on cluster search as preliminary origins if the location fails. Otherwise those origins are ignored. Consider activating "checkOrigins".
- clusterSearch.checkOrigins¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Check, if derived origins fulfill the cluster search criteria anymore. Activating this option may lower the number of events and suppress fake events.
Note
association.* Parameters controlling the association of P and S phases to cluster origins or external origins.
- association.minPhase¶
Default:
4Type: int
Number picks in cluster origin to be reached for starting to associate more P and S picks.
- association.maxDist¶
Default:
1000.0Unit: km
Type: double
Maximum distance from origin to stations for associating P and S picks.
- association.stationConfig¶
Type: file
The station configuration file contains lines consisting of network code, station code, weight (0 or 1) and maximum association distance given in degree. The maximum association distance is the distance in degrees from the origin up to which this station may contribute to a new origin. This parameter overrides the global parameter "association.maxDist". If this distance is 180 deg, this station may contribute to new origins world-wide. However, if the distance is only 10 degree, the range of this station is limited. This is a helpful setting in case of mediocre stations in a region where there are numerous good and reliable stations nearby. The station will then not pose a risk for locations generated outside the maximum association distance. The last item found in the list overrules previous ones. Network and station codes may be wildcards (*) for convenience. Example:
* * 1 10
GE * 1 180
- association.maxPResidual¶
Default:
4.0Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed difference between measured and predicted arrival times for associating P phases to origin. Larger values allow significant correction of initial locations.
- association.dropReferenceCheck¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Allow S-type picks without checking for a reference pick. References to P picks are typically added to S picks by scautopick but picks from other modules may not have this feature. When this option is active, the reference pick is not tested at all. Manual picks are always considered without a reference check.
- association.maxSResidual¶
Default:
4.0Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed difference between measured and predicted arrival time for associating S phases to origins. Larger values allow significant correction of initial locations.
- association.maxResidual¶
Default:
2.0Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum allowed time residuals of picks after association and relocation. Picks will be removed at exceedence starting with largest residual and origins will be relocated.
- association.arrivalCountMinRes¶
Default:
-1Type: int
The number of arrivals of an origin for controlling the association of more picks. Beyond this number, the minimum of maxPResidual or maxSResidual and maxResidual for associating P or S phases, respectively, is tested before association.
The parameter also speeds up the evaluation of origins with more arrivals than configured: Instead of testing residuals of arrivals individually and relocating thereafter, all arrivals not passing the residual check are removed in a bulk.
The parameter is meant to support large-N networks where the high network density results in very many picks and high computational load, effectively slowing down the quality check of picks. Setting a reasonable value, e.g., >20 will only associate the best picks to origins already well constraint.
Using values <= 0 deactivates the feature.
- association.tableType¶
Default:
LOCSATType: string
Values:
LOCSAT,libtau,homogeneousType of travel-time tables for phase association. May be different from locator.
- association.table¶
Default:
iasp91Type: string
Values:
iasp91,iasp91_scanlocName of travel-time table used for phase association. May be different from locator profile. Using a different table/profile may result in increased runtime.
- association.zeroWeightProfiles¶
Type: list:string
zeroWeight-profile name for associating the configured phases with zero weight to origins. Multiples profile names may be set separated by comma. The order of names determines order of checked phases. Each profile can have different parameters.
Note
association.zeroWeight.* Zero-weight profiles containing the parameters for associating phases with zero weight to origins.
Note
association.zeroWeight.$name.*
$name is a placeholder for the name to be used and needs to be added to zeroWeight.profiles to become active.
zeroWeight.profiles = a,b
association.zeroWeight.a.value1 = ...
association.zeroWeight.b.value1 = ...
# c is not active because it has not been added
# to the list of zeroWeight.profiles
association.zeroWeight.c.value1 = ...
- association.zeroWeight.$name.phaseType¶
Type: String
One phase type to be associated with zero weight. Examples: PKP or Pdiff.
- association.zeroWeight.$name.minDistance¶
Default:
120.0Unit: degree
Type: double
Minimum distance from origin to stations.
- association.zeroWeight.$name.maxResidual¶
Default:
5.0Unit: s
Type: double
Maximum time residual of the associated phase.
Note
locator.* Parameters controlling the locator for locating scanloc origins.
- locator.type¶
Default:
LOCSATType: string
Values:
External,FixedHypocenter,Hypo71,iLoc,LOCSAT,NonLinLoc,Router,StdLocThe locator type to be used.
- locator.profile¶
Default:
iasp91Type: string
Values:
iasp91,iasp91_scanlocThe locator profile to be used. Using a different profile/table for locating and associating may result in increased runtime.
- locator.fixDepth¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
If enabled, the locator fixes the depth to the configured default value "defaultDepth" in case that all previous attempts to relocate fail. This option may result in many more origins. It prevents "ignoreDepth" from beeing effective if "defaultDepth" < "ignoreDepth".
- locator.forceFixDepth¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
If enabled, the locator is forced to fix the depth to the value configured by "defaultDepth". Free-depth solutions are thus excluded. Activating this option may be useful for sources with known depths or in case of sparse networks.
Note
eventAssociation.* Parameters controlling the association of interval scanloc origins to internal scanloc events.
- eventAssociation.compareAllArrivalTimes¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
This parameter is only used in conjunction with "eventAssociation.maximumMatchingArrivalTimeDiff". If a station has multiple associated arrivals for a particular event, this flag defines if the time distance of a new pick to all arrivals must be within "eventAssociation.maximumMatchingArrivalTimeDiff" or if one matching arrival is enough.
- eventAssociation.minMatchingArrivals¶
Default:
3Type: int
Minimum number of matching picks between two origins to be associated to the same event.
- eventAssociation.maxMatchingArrivalTimeDiff¶
Default:
-1Unit: s
Type: double
If this time window in seconds is negative, pickIDs are compared to find matching arrivals. A non negative value (including 0) compares pick times regardless of the pickID. Pass: |pick1.time - pick2.time| <= threshold.
- eventAssociation.maxDist¶
Default:
500.0Unit: km
Type: double
Allowed difference in epicenter between an incoming origin compared with preferred origins to get associated.
- eventAssociation.maxTimeSpan¶
Default:
60.0Unit: s
Type: double
Associates an origin with an existing event if the origin time differs not more than 60 seconds unless the minimumMatchingArrivals criteria matches.
Note
publication.* Parameters controlling the publication delay of origin for internal events to the messaging system. The delay time, t, is calculated as t = a x N + b where N is the number of arrivals of the origin. After t seconds, the best origin is published. The first origin is always published.
- publication.intervalTimeSlope¶
Default:
0.5Unit: s/count
Type: double
Parameter "a" in the equation t = a x N + b.
Increasing the value reduces the amount of sent origins. With the option --ep (playback mode) this value is set to 0.
- publication.intervalTimeIntercept¶
Default:
0.0Unit: s
Type: double
Parameter "b" in the equation t = a x N + b.
Increasing the value reduces the amount of sent origins. With the option --ep (playback mode) this value is set to 0.
- publication.wakeUpInterval¶
Default:
5Unit: s
Type: int
Integer interval to check the origin buffer for sending origins if no other origins have been created.
Reducing the value may be required in EEW: it increases the load on scanloc but allows to send origins more rapidly.
ScoreMF plugin¶
Plugin for computing a score for an origin by the OriginMultiFeature score processor.
Note
score.mf.* The origin score processor “OriginMultiFeature” returning a score for an origin as a measure of goodness. The score is then compared against minScore.
Add the plugin “scoremf” to the global parameter “plugins”, set the scanloc parameter “score” to “OriginMultiFeature” for applying this score processor and adjust “minScore” and “score.mf.” accordingly.*
- score.mf.defaultScore¶
Default:
0.0Type: double
The default score returned for an origin that fails completely or is filtered out by thresholds such as for depth and RMS.
- score.mf.scoreManualOrigins¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Compute the score also for manual origins. When inactive, manual origins are returned with default score and may never become preferred among other internal origins.
- score.mf.ignoreDepth¶
Default:
650.0Type: double
This is the maximum allowed depth. Origins with greater depths get a score equal to "defaultScore".
- score.mf.maxRMS¶
Default:
1.5Type: double
This is the maximum allowed RMS. Origins with greater residuals get a score equal to "defaultScore".
- score.mf.strongMotionCodes¶
Default:
L,NType: list:string
List of one-letter instrument codes (2nd letter) in channel codes identifying strong motion sensors, e.g., in HL?, HN?.
- score.mf.infrasoundCodes¶
Default:
DType: list:string
List of one-letter instrument codes (2nd letter) in channel codes identifying infrasound sensors, e.g., in HDF.
- score.mf.weights.p¶
Default:
1.0,0.0,0.0Type: list:double
The weight for number of used P arrival measures. Assumes only arrival time when exactly 1 value is set. Use a comma-separated list, wT,wSlo,wBaz, for giving specific weight to pick time, slowness and back azimuth, respectively. Example: 1.0,0.0,0.0
- score.mf.weights.p0¶
Default:
0.5Type: double
Weight per unused P pick.
- score.mf.weights.s¶
Default:
2.0Type: double
Weight per used S pick.
- score.mf.weights.s0¶
Default:
0.5Type: double
Weight per unused S pick.
- score.mf.weights.normalizationDepth¶
Default:
650.0Type: double
Origin depth is normalized to this value for computing the score contribution. Shallower depths contribute to larger score.
- score.mf.weights.depth¶
Default:
1.0Type: double
Weight for depth-based quality score.
- score.mf.weights.normalizationRMS¶
Default:
1.5Type: double
Origin RMS is normalized to this value for computing the score contribution. Lower RMS contribute to larger score.
- score.mf.weights.residual¶
Default:
1.0Type: double
Weight for RMS-based quality score.
- score.mf.weights.gap¶
Default:
1.0Type: double
Weight for azimuthal gap score. The smaller the gap the larger the score.
- score.mf.weights.manualPick¶
Default:
0.5Type: double
Weight per used manual pick.
- score.mf.weights.strongMotion¶
Default:
0.0Type: double
Weight per used strong motion pick as defined in "strongMotionCodes".
- score.mf.weights.infrasound¶
Default:
0.0Type: double
Weight per used infrasound pick as defined in "infrasoundCodes".
- score.mf.weights.authors¶
Unit: author:score
Type: list:string
List of tuple of authors and score contribution. If an author matches, the corresponding score contribution is added to the final score.
Example: "scautoloc:1,scanloc:10,ccloc:100".
ScoreSum plugin¶
Plugin for scoring origins in scanloc by score processor OriginSum
Note
score.sum.* The origin score processor “OriginSum”: Compute origin scores as weighted averages of number of used P phases (p), number of unused P phases (p0), number of used S phases (s), number of unused S phases (s0), origin depth and residual. The score applies for ranking origins of events.
Add the plugin “scoresum” to the global parameter “plugins” and “OriginSum” to the scanloc parameter “score” for applying this score processor and adjust “minScore” and “score.sum.” accordingly.*
- score.sum.scoreManualOrigins¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Compute the score also for manual origins. When inactive, manual origins are returned with score = 0 and may never become preferred among other internal origins.
- score.sum.p¶
Default:
1.0Type: list:double
The weight for number of used P arrival measures. Assumes only arrival time when exactly 1 value is set. Use a comma-separated list, wT,wSlo,wBaz, for giving specific weight to pick time, slowness and back azimuth, respectively. Example: 1.0,0.0,0.0
The usage of slowness and back azimuth depends on locator. They are not considered by Hypo71, NonLinLoc, StdLoc and FixedHypocenter.
The parameter is used for Is infrasound phases when considered in clustering.
- score.sum.p0¶
Default:
0.5Type: double
The weight for number of added but unused P arrivals.
The parameter is used for Is infrasound phases when considered in clustering.
- score.sum.s¶
Default:
2.0Type: list:double
The weight for number of used S arrival measures. Assumes only arrival time when exactly 1 value is set. Use a comma-separated list, wT,wSlo,wBaz, for giving specific weight to pick time, slowness and back azimuth, respectively. Example: 2.0,0.0,0.0
The usage of slowness and back azimuth depends on locator. They are not considered by Hypo71, NonLinLoc, StdLoc and FixedHypocenter.
- score.sum.s0¶
Default:
0.5Type: double
The weight for number of added but unused S arrivals.
- score.sum.normalizationDepth¶
Default:
650.0Unit: km
Type: double
Origin depth is normalized to this value for computing the score contribution. Shallower depths contribute to larger score.
- score.sum.depth¶
Default:
1.0Type: double
The weight of origin depth. Set this value to 0.0 for scoring origins independent of depth whenever shallow and deep sources are equally expected.
- score.sum.normalizationRMS¶
Default:
1.5Unit: s
Type: double
Origin RMS is normalized to this value for computing the score contribution. Lower RMS contribute to larger score.
- score.sum.residual¶
Default:
1.0Type: double
The weight of origin RMS residual.
- score.sum.increaseManual¶
Default:
falseType: boolean
Increase the weight for manual picks by a factor of 1.001. This gives preference to manual picks in case automatic ones co-exist for the same station.
Command-Line Options¶
scanloc [options]
Generic¶
- -h, --help¶
Show help message.
- -V, --version¶
Show version information.
- --config-file file¶
The alternative module configuration file. When this option is used, the module configuration is only read from the given file and no other configuration stage is considered. Therefore, all configuration including the definition of plugins must be contained in that file or given along with other command-line options such as --plugins.
- --plugins arg¶
Load given plugins.
- -D, --daemon¶
Run as daemon. This means the application will fork itself and doesn’t need to be started with &.
Verbosity¶
- --verbosity arg¶
Verbosity level [0..4]. 0:quiet, 1:error, 2:warning, 3:info, 4:debug.
- -v, --v¶
Increase verbosity level (may be repeated, e.g., -vv).
- -q, --quiet¶
Quiet mode: no logging output.
- --print-component arg¶
For each log entry print the component right after the log level. By default the component output is enabled for file output but disabled for console output.
- --component arg¶
Limit the logging to a certain component. This option can be given more than once.
- -s, --syslog¶
Use syslog logging backend. The output usually goes to /var/lib/messages.
- -l, --lockfile arg¶
Path to lock file.
- --console arg¶
Send log output to stdout.
- --debug¶
Execute in debug mode. Equivalent to --verbosity=4 --console=1 .
- --trace¶
Execute in trace mode. Equivalent to --verbosity=4 --console=1 --print-component=1 --print-context=1 .
- --log-file arg¶
Use alternative log file.
Messaging¶
- -u, --user arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
connection.username.
- -H, --host arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
connection.server.
- -t, --timeout arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
connection.timeout.
- -g, --primary-group arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
connection.primaryGroup.
- -S, --subscribe-group arg¶
A group to subscribe to. This option can be given more than once.
- --start-stop-msg arg¶
Default:
0Set sending of a start and a stop message.
Database¶
- --db-driver-list¶
List all supported database drivers.
- -d, --database arg¶
The database connection string, format: service://user:pwd@host/database. "service" is the name of the database driver which can be queried with "--db-driver-list".
- --config-module arg¶
The config module to use.
- --inventory-db arg¶
Load the inventory from the given database or file, format: [service://]location .
- --db-disable¶
Do not use the database at all.
Input¶
- --ep arg¶
Type: string
Name of input XML file (SCML) with all picks and origins for offline processing. The database connection is not received from messaging and must be provided. Results are sent as XML to stdout.
- --timing arg¶
Default:
pickTimeValues:
creationTime,pickTimeTiming reference in offline processing with --ep: Use pickTime and creationTime for sorting picks according to pick time and creation time, respectively. pickTime is assumed if no timing is specified. Note: In real-time processing picks are treated as they arrive corresponding to creationTime and this option is irrelevant.
Buffer¶
- --allow-rejected-picks¶
Allow processing of picks with evaluation status ‘rejected’. Otherwise these picks are ignored and not buffered.
- --drop-reference-check¶
Overrides configuration parameter
association.dropReferenceCheck.
- --author-whitelist arg¶
Type: list:string
Only consider picks and origins created by the given author(s). Separate multiple authors by comma. Wildcards are supported.Empty strings allow all authors. Manual origins are treated regardless of the author as defined by "buffer.ignoreManualOrigins". The option allows operating scanloc based on picks and origins from a specific module, e.g., in a pipeline.
- --future-time-delta arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
buffer.futureTimeDelta.
- --origin-keep arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
buffer.originKeep.
- --pick-keep arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
buffer.pickKeep.
Locator¶
- --locator-type arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
locator.type.
- --locator-profile arg¶
Overrides configuration parameter
locator.profile.Type: string
- --locator-list¶
List all registered locators.
Output¶
- --final-only¶
Limit result set to final origins only. This option is available for non-real-time (--ep) processing only.
- --dump-origins¶
Don’t publish origins, write them to stdout. Useful for tuning.
- --cluster-search-log-file arg¶
Type: string
File name to output detailed cluster search information. Useful for tuning.
- -f, --formatted¶
Use formatted XML output along with ‘--ep’. Otherwise XML is unformatted.