Help! I’m stuck! Now what?¶
You will …
Troubleshoot and resolve problems with SeisComP
Pre-requisites for this tutorial:
Have your SeisComP installation and configuration available
Afterwards/Results/Outcomes:
Improved understanding of ways to solve issues when operating SeisComP
Time range estimate:
30 minutes
Outline¶
Inevitably you will encounter difficulties using SeisComP. This tutorial reviews a few ways to diagnose your problems and get help to resolve them:
Detailed HTML documentation
The SeisComP Forum
Reviewing logging options
Ways to diagnose and to get help¶
HTML documentation¶
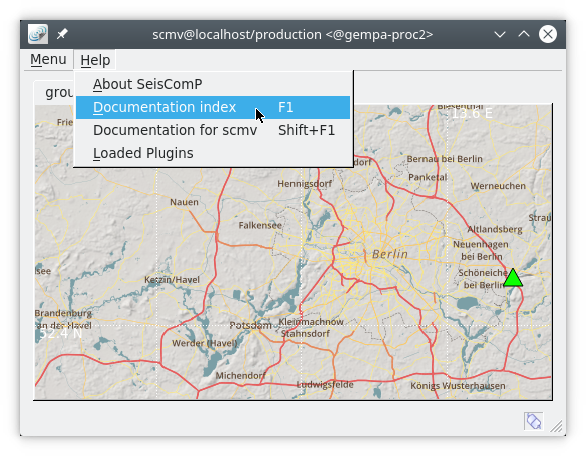
Most modules have HTML documentation. When installed, it can be found in scconfig under Docs. The HTML documentation can also be reached from the Help menu of all GUIs. It contains the description of configuration and command-line parameters along with an overview with many detailed information.
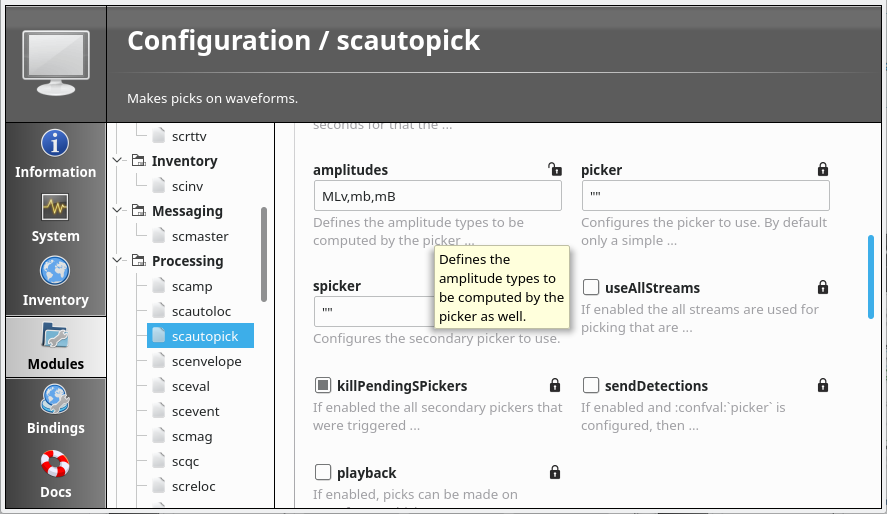
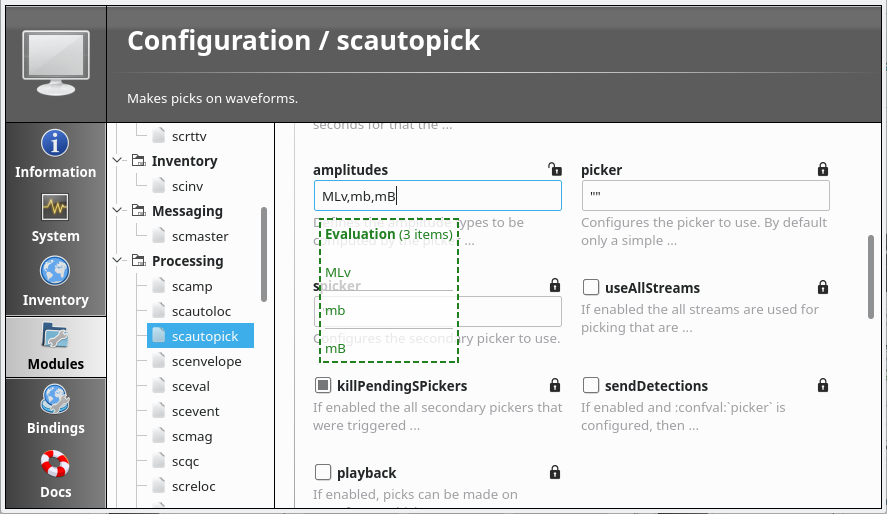
The description of most configuration parameters is also available from within scconfig. Look under Modules, and choose the relevant module. For each parameter, the first few lines of description are shown; hovering over these reveals the full text.
The HTML documentation is built regularly and available online, e.g. gempa’s documentation.
Commandline help¶
In addition to the HTML documentation, many SeisComP commands have manual pages which can be read on the command line:
$ man [module name]
and help on command-line options:
$ [module name] -h
Note
The command-line option -h can be used with almost all modules. No matter how many other command-line parameters were given, -h will stop the module and print the help on the command-line.
Configuration parameters¶
The scconfig GUI tool can be conveniently used to adjust the module and bindings configuration. It also displays help on each individual configuration parameter for every module. Read the concepts section on configuration for a comprehensive overview.
Command-line parameters¶
Command-line parameters provide additional flexibility when executing modules. To learn about them read the HTML documentation or execute
$ [module name] -h
The SeisComP Forum¶
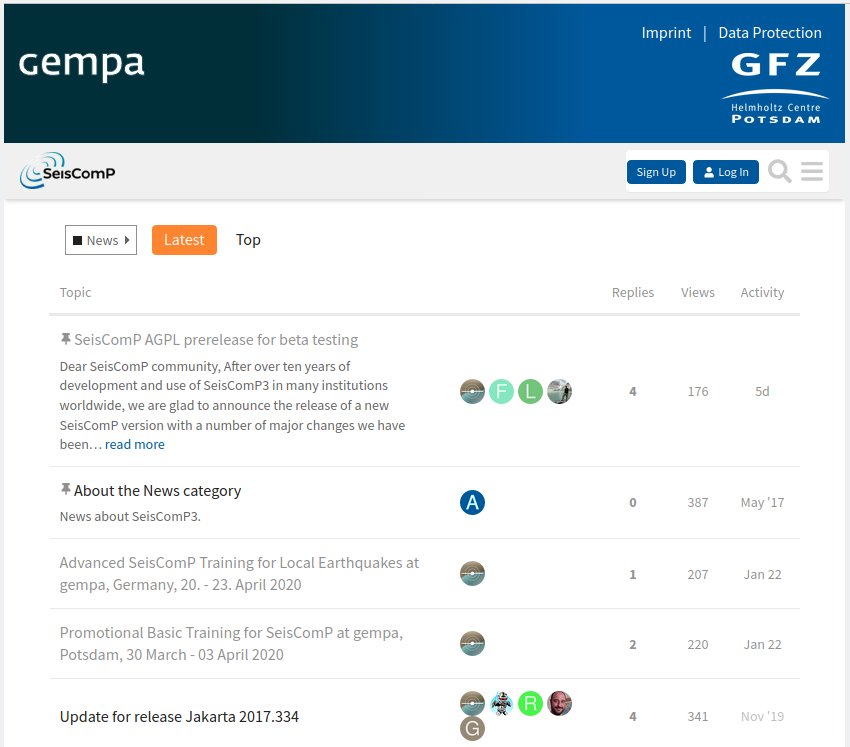
The SeisComP forum [23] is the place to discuss SeisComP. Announcements about updates, training courses and more are posted here by the developers, and users can post questions or discuss new developments. Anyone can browse the forum, while registration is required to post there.
If you have specific technical problems, it helps to have tried some of the ideas below. Please include version information (the ‘-V’ option described below) if you report a problem.
Logging¶
Most SeisComP applications use a standard logging approach.
By default, they log to files in your ~/.seiscomp/log directory,
such as scamp.log.
Further options for logging are described in
Configuration.
You can control how often these are rotated (old log files are closed, and moved to a new file name, such as scamp.log.1, e.g. daily). Alternatively you can use the system-wide logging facility syslog and send logs to /var/log or another “standard” place.
There are four levels of severity of SeisComP log messages, and applications can be configured to show only those which are more severe than a given threshold.
1 = ERROR
2 = WARNING
3 = INFO
4 = DEBUG.
Default is 2. Setting logging.level = 4 results in the most messages.
For other modules such as seedlink, the log files are written to
seiscomp/var/log/
Debugging options¶
Most SeisComP applications support two important command line options:
Use –console to send output to the terminal instead of the usual log location.
-v for increased verbosity, or use –verbosity= n where n is one of the four severity levels above.
In addition:
–debug sets logging.level (see above) to 4 (DEBUG), and sends logging output to the console (terminal) instead of the usual log location. (This is just an easier way of specifying –verbosity=4 –console=1.) For example:
$ ~/seiscomp/bin/seiscomp exec scmag --debug 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: . 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/.seiscomp/plugins 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/lib/plugins 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/lib 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/share/plugins 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/lib 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/lib 11:47:50 [debug] Adding plugin path: /home/user/seiscomp/share/plugins/scmag 11:47:50 [debug] Trying to open plugin at /home/user/seiscomp/share/plugins/dbmysql.so 11:47:50 [info] Plugin dbmysql registered 11:47:50 [info] Plugins: -------- [1] description: MySQL database driver author: GFZ Potsdam <seiscomp-devel@gfz-potsdam.de> version: 0.9.2 API: 12.1.0 11:47:50 [info] Connect to messaging 11:47:50 [debug] Trying to connect to scmag@localhost with primary group = MAGNITUDE 11:47:50 [info] Connecting to server: localhost 11:47:50 [info] Connected to message server: localhost 11:47:50 [info] Joining MASTER_GROUP group 11:47:50 [info] Sending connect message to server: localhost 11:47:51 [info] Server version is 'Jakarta 2018.327.p15' 11:47:51 [info] Outgoing messages are encoded to match schema version 0.11 11:47:51 [info] user "scmag" connected successfully to localhost
The above reveals that scmag was able to load, and connect to the messaging system. Note that the verbosity of each message (“info”, “debug”, etc) is also shown. However a moment later we see:
11:47:51 [info] Connect to database 11:47:51 [debug] skipping unknown network message 11:47:51 [debug] skipping unknown network message 11:47:51 [debug] skipping unknown network message 11:47:56 [error] Timeout while waiting for database provide message 11:47:56 [debug] Leaving ::done 11:47:56 [info] Shutting down MagTool - database accesses while runtime: 0
This suggests that scmaster was not running to provide a connection to the database. To resolve this, you could next check that scmaster is running as expected.
Note
Instead of –debug in the example above, you could run
$ ~/seiscomp/bin/seiscomp exec scmag -vvvv
The output is the same, but it is sent to your normal logging file, typically ~/.seiscomp/log/scmag.log.
In scconfig, logging can be set globally. Go to the Modules tab, then System > global (see “logging”) or per module.
e.g. set “logging.level = 3” in $SEISCOMP_ROOT/etc/scamp.log to set level to INFO only for scamp.
You should also be aware of the version of SeisComP that you are running. The ‘-V’ or ‘–version’ option provides this for many SeisComP modules.
$ ~/seiscomp3/bin/seiscomp exec scmag -V
scmag: Jakarta 2018.327.p15
API version: 12.1.0
GIT HEAD:
Compiler: c++ (Ubuntu 7.3.0-16ubuntu3) 7.3.0
Build system: Linux 4.15.0-20-generic
OS: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS / Linux
Commercial support¶
Professional commercial support to SeisComP users is available from gempa GmbH [26].
Next time you have a problem¶
Try some of the above techniques.
If you find a solution, don’t forget to share it at the SeisComP forum [23].