A continuously updated multi-event relocated catalog
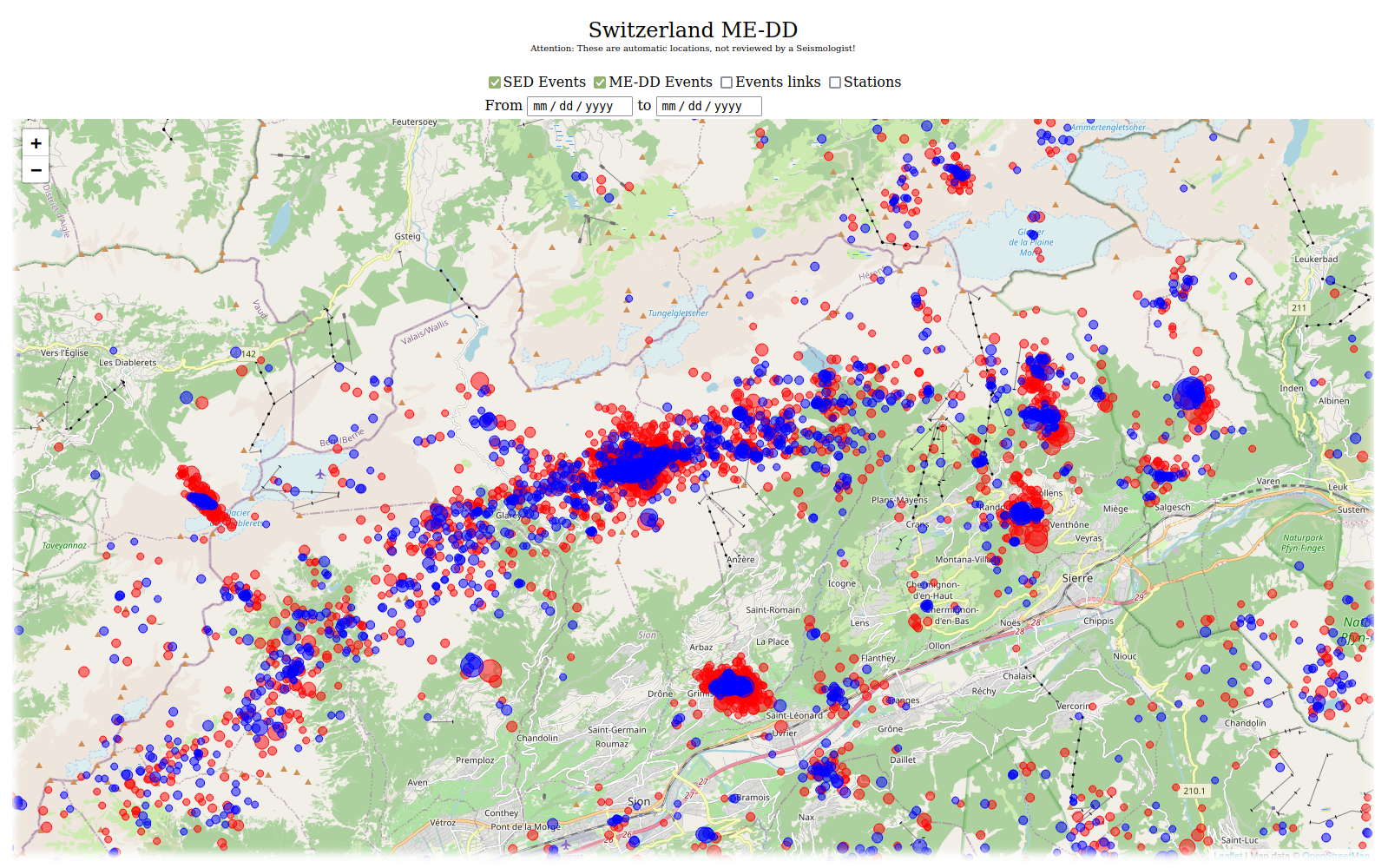
Thanks to the integration with SeisComP, it is straightforward to use rtDD to periodically generate a double-difference catalog of a region, ensuring that recent events are continuously included in the double-difference inversion. This is useful not only for maintaining up-to-date snapshots of high-resolution earthquake locations (multi-event) but is also crucial for real-time double-difference inversion, where new origins are relocated relative to a reference catalog. Without an up-to-date reference catalog, real-time relocations may become inaccurate or impossible, particularly in areas lacking historical reference events. This is especially important when monitoring regions where historical seismicity is unknown.
For this reason, the generate-reference-catalog.sh script (located in this folder) is provided. It can be easily adapted to specific use cases and is useful for periodically generating a multi-event relocated catalog, which can also be displayed on an interactive map.
A recommended workflow is to rebuild the reference catalog on a periodic basis (e.g., weekly). The reference catalog is typically built starting from manually reviewed absolute location events (the preferred origins in the SeisComP database). In this workflow the rtDD origins are never set as preferred, as these real-time single-event rtDD solutions become outdated once a new reference catalog is computed.
In this configuration, the real-time rtDD solutions, together with the rtDD reference catalog, serves as a complementary product to the traditional absolute location catalog.
A visualization system might display the latest reference catalog together with the current week’s real-time rtDD solutions (which are not yet integrated into the reference). In the subsequent relocation cycle, these recent events are incorporated into the updated reference catalog. Thus, the scrtdd catalog is best utilized as an evolving and complementary resource.