Application and Setup¶
The tasks of DeepC can be applied along with phase picking in scautopick,
screpick and scolv or the corresponding module aliases. To make them
available to a module add the plugin in the global configuration
(global.cfg or the specific module configuration, e.g. of scautopick,
scautpick.cfg) like:
plugins = ${plugins}, deepc
Depending on the module, a module configuration may be required to define the
specific tasks of deepc. However, the specific configuration of DeepC is done
by global bindings parameters residing under picker.deepc and
spicker.deepc.
Note
By adding a line like
module.trunk.global.<parameter> = <value>in a module configuration file, each global binding parameter <parameter> is set globally for all stations. This kind of parameters overrides any configured station binding and the configuration is not supported by scconfig [13].In the following, many of the example configurations will for simplicity be presented as globally set in a module configuration file. In production, you should configure your global binding profiles instead.
Example: scautopick¶
The main module using DeepC is scautopick.
As shown in fig-deepc-workflow-scautopick, scautopick forwards
detections to DeepC, which extracts waveforms in a window around the initial
trigger. DeepC then feeds the data to the loaded DL model and generates
the output according to the model type and configuration.
The DeepC package ships with 4 kinds of sub-pickers (tasks): 3 primary pickers DeepC-EC, DeepC-PC, DeepC-PR and a secondary picker DeepC-SR. Each sub-picker has its own configurable global binding parameter group. See this table for an overview.
To start scautopick with DeepC, define one of the sub-pickers to be applied to
P and S phases by adjusting the module parameters picker and
spicker, respectively. Example (scautopick.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins}, deepc
# picker = deepc-ec
# picker = deepc-pc
picker = deepc-pr
spicker = deepc-sr
In regular operation you should no activate the scautopick parameter
sendDetections which suppresses emitting initial triggers in addition
to DeepC’s picks. However, activating this parameter can be really helpful for
tuning and debugging.
Add a global or scautopick binding or edit an existing one for configuring a
sub-picker.
In scconfig, navigate to Bindings, choose a global or scautopick binding and
search (Ctrl-F) for “deepc”. Set the picker.deepc.modelsPath and
spicker.deepc.modelsPath when re-picking P and S picks, respectively,
and consider the remaining parameters in the sub-picker’s section.
There are also other common parameters which are less important. Their application will be discussed later. Further, you need to specify the model to use in each case. You find a collection of available models here.
For an offline playback, run scautopick with your miniSEED data file writing the output picks to a well-formed SCML file.
scautopick -I data.mseed --ep --playback --debug > picks.xml
Task 1: Event type¶
Currently no event classification model is provided by gempa. Once you have access to an appropriate model, follow these steps to use it.
scautopick¶
Add to your module configuration file (scautopick.cfg):
picker = "deepc-ec"
The next step is to choose a model that suits your data (currently none is available) and edit other parameters if needed.
picker.deepc.deepcEC.modelWeights- this is the name of the chosen model (“weights”)picker.deepc.deepcEC.picker- edit if you want another, conventional picker like AIC as intermediate picker; you could keep your existing settings as they are by setting your preferred picker here instead of its usual configuration (deepc-config-example-scautopick, line 3); DeepC will then classify the wrapped picker’s pick instead of the STA/LTA triggerpicker.deepc.deepcEC.threshold- edit if you want to use a custom confidence threshold that labels picks not surpassing it as ‘Noise’.
A comment will be added with the proposed signal classification.
screpick¶
Use screpick to classify the signal type of picks. In this case, you can skip creating bindings and
add the model to use globally directly in the screpick configuration (screpick.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins}, deepc
picker = deepc-ec
anyPhase = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcEC.modelWeights = <classification_model>
Now, just provide the file with already calculated picks and apply event classification using your preferred model:
screpick --debug -I data.mseed --ep picks.xml -f > classified-picks.xml
Note
Ensure screpick’s parameter anyPhase is set. If unsure, add -A to the command.
The output file classified-picks.xml will contain the same picks provided with a comment about the event classification per pick.
Output¶
Example section of the output XML:
[...]
<comment>
<text>earthquake</text>
<id>deepc:eventTypeHint</id>
</comment>
[...]
To a add comment containing the confidence value of the classification,
activate parameter picker.deepc.addComment.
Task 2: Phase type¶
scautopick¶
Add to your module configuration (scautopick.cfg):
picker = "deepc-pc"
Choose a model that suits your data (currently only one is available) and edit the other parameters as needed.
picker.deepc.deepcPC.modelWeights- this is the name of the chosen model (“weights”)picker.deepc.deepcPC.picker- edit if you want another, conventional picker like AIC as intermediate picker; you could keep your existing settings as they are by setting your preferred picker here instead of its usual configuration (deepcPC-config-example-scautopick, line 3); DeepC will then classify the wrapped picker’s pick instead of the STA/LTA triggerpicker.deepc.deepcPC.threshold- edit if you want to use a custom confidence threshold that labels picks not surpassing it as ‘Noise’.
The phase hint of the pick will change if the model re-classifies it. In case of noise, no pick will be
emitted unless you turn on picker.deepc.sendNoise.
screpick¶
If you have picks whose phases you like to (re)classify, you can skip bindings and, for convenience,
add the model to use globally in the screpick configuration (screpick.cfg):
plugins = ${plugins}, deepc
picker = deepc-pc
anyPhase = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPC.modelWeights = <classification_model>
Now, add your file with already calculated picks and screpick will apply phase classification using your preferred model:
screpick --debug -I data.mseed --ep picks.xml -f > classified-picks.xml
Note
Activate the screpick configuration parameter anyPhase. If unsure, add
-A to the command.
Output¶
If the pick is not classified as noise, the phaseHint will be reset to the new phase.
If picker.deepc.addComment is active, a comment will be added containing
the old and the new phase hint as well as the confidence, e.g
(classified-picks.xml):
[...]
<comment>
<text>PC: P -> S: 95.53%</text>
<id>deepc</id>
</comment>
[...]
Task 3: Phase type and pick time refinement¶
scautopick¶
Set scautopick parameter picker to DeepC-PR
picker = "deepc-pr"
Choose a model that suits your data and configure the other parameters as needed.
picker.deepc.deepcPR.modelWeights- this is the name of the chosen model (“weights”)picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalBegin,picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalEnd,picker.deepc.deepcPR.S.signalBegin,picker.deepc.deepcPR.S.signalEnd- always adjust these values not only to your data, but also in compliance with the input length of the chosen model; e.g., for a model with only 5s input, reasonable restriction intervals could befor P and
for S. DeepC-PR will only look for pick inside this range. See section Restricting the picking range for details.
picker.deepc.deepcPR.threshold- if you want to overwrite the model’s recommended confidence thresholds; reasonable values ranges from 0.1 to 0.9; in most cases, 0.3 is good start unless the model has already a recommended value which you can find out by leaving these parameters at -1; 0.1 would be the default if nothing was set or found in the models config file. Note that you can set P and S threshold separately. Look up the parameter for details on the configuration syntax.
The pick time will be changed to the refined time and the phase hint of the
pick will change in case the model re-classifies it. In case of noise,
no pick will be emitted unless you turn on picker.deepc.sendNoise.
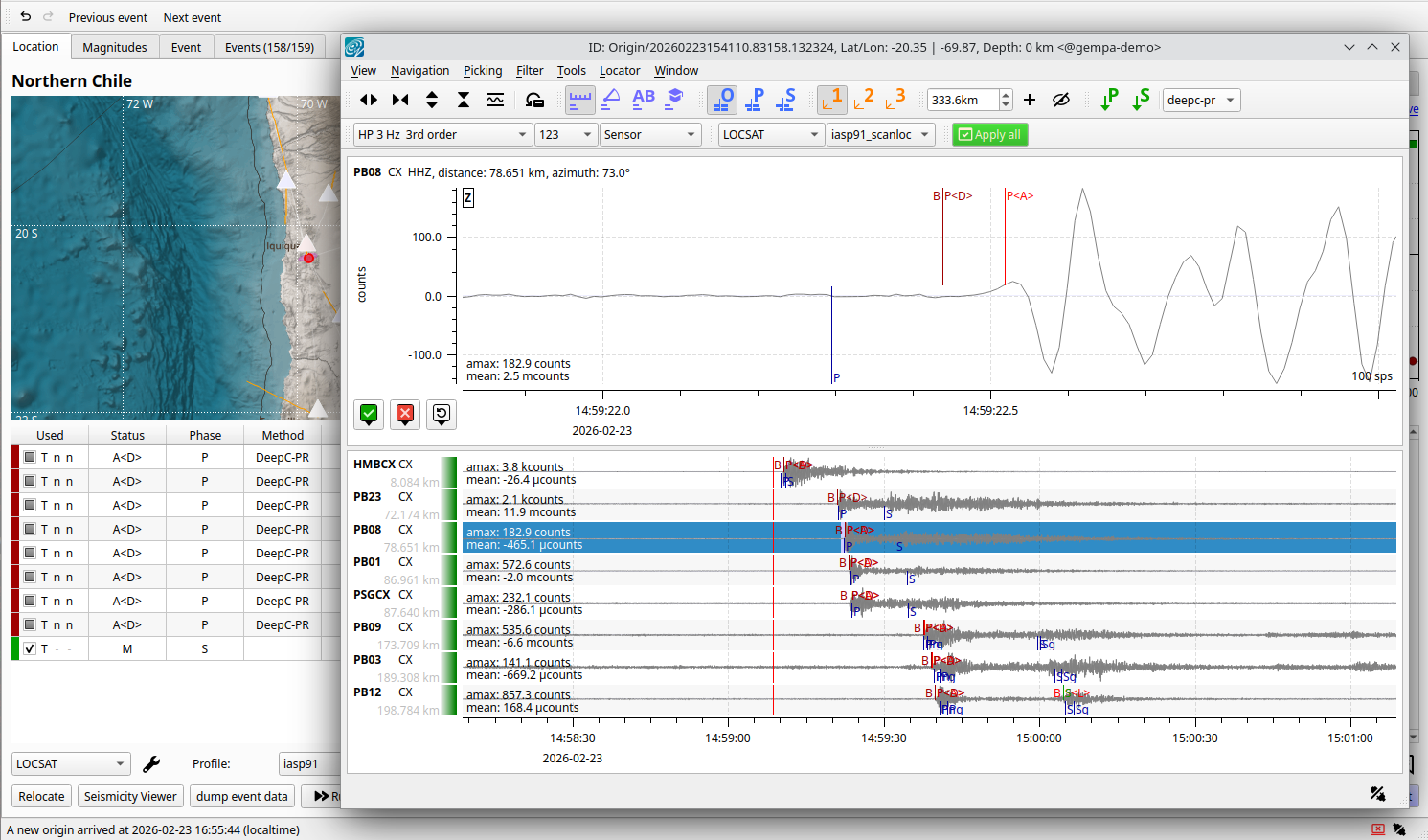
Figure 35: Picks made with deepc are identified in scolv by the method shown in the phase table and abbreviated by D along with picks on seismograms.¶
S picks¶
DeepC is not restricted to being the primary picker. It can also be used to create S picks which will reference the P pick produced by a primary picker. This can be achieved by using the special sub-picker DeepC-SR as secondary picker:
spicker = "deepc-sr"
As secondary picker, DeepC-SR takes the same trigger as DeepC-PR, but cuts a window slightly to the advantage of a potential S pick, applies DL inference and returns the first S pick after the trigger.
Note
You can conveniently use DeepC-PR and DeepC-SR in the same run as picker and spicker, respectively. But in case DeepC-PR reclassifies a P pick as S, there is a chance that you get two S picks when DeepC-SR sees and emits the same S pick, this is because both instances work independently from each other.
In the resulting pick object, the phase hint will be changed. Additionally, the phase classification can be found
with the model’s confidence, in a comment when picker.deepc.addComment is active.
screpick¶
screpick [16] focuses on P picks and you cannot use DeepC-SR as secondary picker.
Instead, DeepC-PR sufficiently generates S picks in reclassification mode although it may prefer P picks
over S picks.
Here is an example configuration (screpick.cfg) using PhaseNet trained
on STEAD (“pn-st”):
plugins = ${plugins}, deepc
picker = deepc
anyPhase = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepcPR.reclassify = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepcPR.modelWeights = pn-st
Note that anyPhase should be enabled otherwise S picks won’t be processed.
screpick --debug -I data.mseed --ep picks.xml -f > repicks.xml
Warning
If you turn off picker.deepc.deepcPR.reclassify but leave screpick’s
parameter anyPhase enabled, DeepC-PR may be also fed with S picks, but then
an S pick might be “corrected” to the time of a potential P pick, because DeepC-PR
can’t see the original phase hint. So it guesses that this pick was way off
from the intended P pick and it will change the pick time accordingly,
although this pick was supposed to mark an S onset.
(This restriction might change in the future)
Here is a comprehension of use cases:
Purpose |
anyPhase |
reclassify |
comment |
|---|---|---|---|
Repick P phases only |
false |
false |
|
Repick S phases only |
not possible |
||
Repick P and S phases |
true |
true |
Output:
The phase hint of the pick will change if the model re-classifies it.
In case of noise, no pick will be emitted unless you turn on
picker.deepc.sendNoise. The confidence can be added in a
comment via picker.deepc.addComment.
scolv¶
You can use DeepC as interactive re-picker inside the scolv waveform picker window.
Since most picker models need three components, it is therefore necessary to load them in scolv by
pressing ‘T’ (followed by ‘E’ and ‘N’ for horizontal components to show up), or
use the scolv parameter picker.loadAllComponents.
Remember to unset the filter before repicking due to most models being trained on
raw waveform data or having their own filter preprocessor.
It is advisable to only repick filtered data when the model couldn’t find a
pick in the raw data.
You can pick both, P and S onsets, but currently the only available sub-picker for both is DeepC-PR, which has a preference for P picks.
To explicitly tell DeepC-PR to only pick P onsets, turn off
picker.deepc.deepcPR.reclassify.
Turn on the same parameter if you want to allow S picks.
Detailed information about the classification is currently only provided
in the terminal.
You will find a message whether a pick was found and whether it was re-classified to S.
Note
In reclassification mode, DeepC-PR will always assume that you wanted to refine a P pick. Have a look into the decision tree for comprehension.
In consequence, DeepC-PR may return a P pick if the confidence for an S pick does not exceed the threshold in the picking range that was specifically allowed for S picks. See next section of how to define this range.
Starting scolv¶
Scolv needs to know how much data it should send to DeepC. Therefore two scolv module parameters have to be set: picker.repickerStart and –picker.repickerEnd. They define the input window for the model relative to the time at the cursor position. This information can be extracted from the model’s config file. Here is an example for PhaseNet(ETHZ):
[...]
39 "time_before_pick_sec": 15.005,
40 "time_after_pick_sec": 15.005,
[...]
time_before_pick_sec and time_after_pick_sec are used by DeepC to cut the window around the trigger. Therefore, adjust the scolv parameters picker.repickerStart and picker.repickerEnd accordingly while keeping in mind that scolv won’t call DeepC unless there is enough data.
In general these values do not vary a lot, default values for PhaseNet are -15.005 and 15.005, for EqTransformer models -30 and 30. You don’t need to be this exact, in fact it is not a bad idea to enlarge the window by a second or two since this helps with the data pre-processing steps.
Example call:
scolv -I data.mseed -i picks.xml --debug
Turn on the debug mode to see your model’s decisions in the terminal while you are repicking with mouse and keyboard.
Confidence output inside scolv GUI¶
By default, the confidence is shown in the SNR field of the marked trace.
If the confidence was too low for the pick, it will be shown as negative number.
To prevent this behavior and get the actual SNR value instead,
deactivate picker.deepc.deepcPR.publishConfidenceAsSnr.
Restricting the picking range¶
In most scenarios it is of advantage to restrict the range of allowed picks in a much narrower window around the cursor in contrast to the full length of the time window fed into DeepC-PR and DeepC-SR. The input window might be so wide that it includes other onsets that you are not interested in. DeepC-PR always returns the pick with the highest confidence in the entire window. This means a pick with a high SNR is very likely to be returned as the most confident pick, but may not be of interest for you. You can force DeepC-PR to only pick inside P.signalBegin and P.signalEnd (S.signalBegin and S.signalEnd respectively) around the cursor in scolv / around the trigger, in general.
Example using scolv repicker 1¶
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.publishConfidenceAsSnr = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalBegin = -5
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalEnd = 4
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.reclassify = false
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.threshold = 0.4
These settings would allow DeepC-PR to return a pick only if it was found between
five seconds before the mouse cursor’s position and 4 seconds after it.
If there is no confidence peak above the given threshold 0.4, DeepC-PR will tell you it’s
noise (in the terminal) even though there might already be A reasonable pick outside of this interval
and inside of the waveform data DeepC-PR was fed with (blue-ish zone).
The SNR field shows the confidence of the model about it’s noise classification
but as negative value.
[SCREENSHOT]
Example using scolv repicker 2¶
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.publishConfidenceAsSnr = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalBegin = -5
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.P.signalEnd = 4
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.reclassify = true
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.S.signalBegin = 0.5
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.S.signalEnd = 10
module.trunk.global.picker.deepc.deepcPR.threshold = 0.4,S:0.3
As the first example, these settings would allow DeepC-PR to return a pick only
if it was found between five seconds before the mouse cursor’s position and 4 seconds after it.
If there is no confidence peak above the given threshold 0.4, DeepC-PR will
check if a potential S pick would be in the range of 0.5 to 10 s after the trigger,
and whether its confidence exceeds the threshold of 0.3.
In Figure .. this is the case, the mouse cursor is moved to position of the
S pick and the SNR field shows the confidence of the classification.
[SCREENSHOT]
Filtering waveforms before input¶
Most models are not trained on filtered waveform data and require raw data since filters are already encoded within the models parameters by training. However, some data might benefit from filtering. Use these parameters carefully.
The value must comply with the usual SeisComP filter syntax. [LINK?]
Treating problematic data¶
The following descriptions are valid not only for parameter group picker.deepc, but also for spicker.deepc.deepcSR.
Ranges of zeros in waveforms can be a problem for DL models as their predictions are not reliable.
You can define the length of leading zeros that falsifies a pick in the parameter group
picker.deepc.pickFalsification.
This check is performed for the pick (or trigger) that DeepC receives on start,
such that, when the check fails, it won’t process the waveforms and won’t send the initial pick.
To send the initial pick regardless of the zero-check, set parameter picker.deepc.sendRejected.
Set picker.deepc.pickFalsification.signalBegin to define the window start relative to the trigger.
Set picker.deepc.pickFalsification.zeros to define the number of adjacent zeros to look for in this
window.